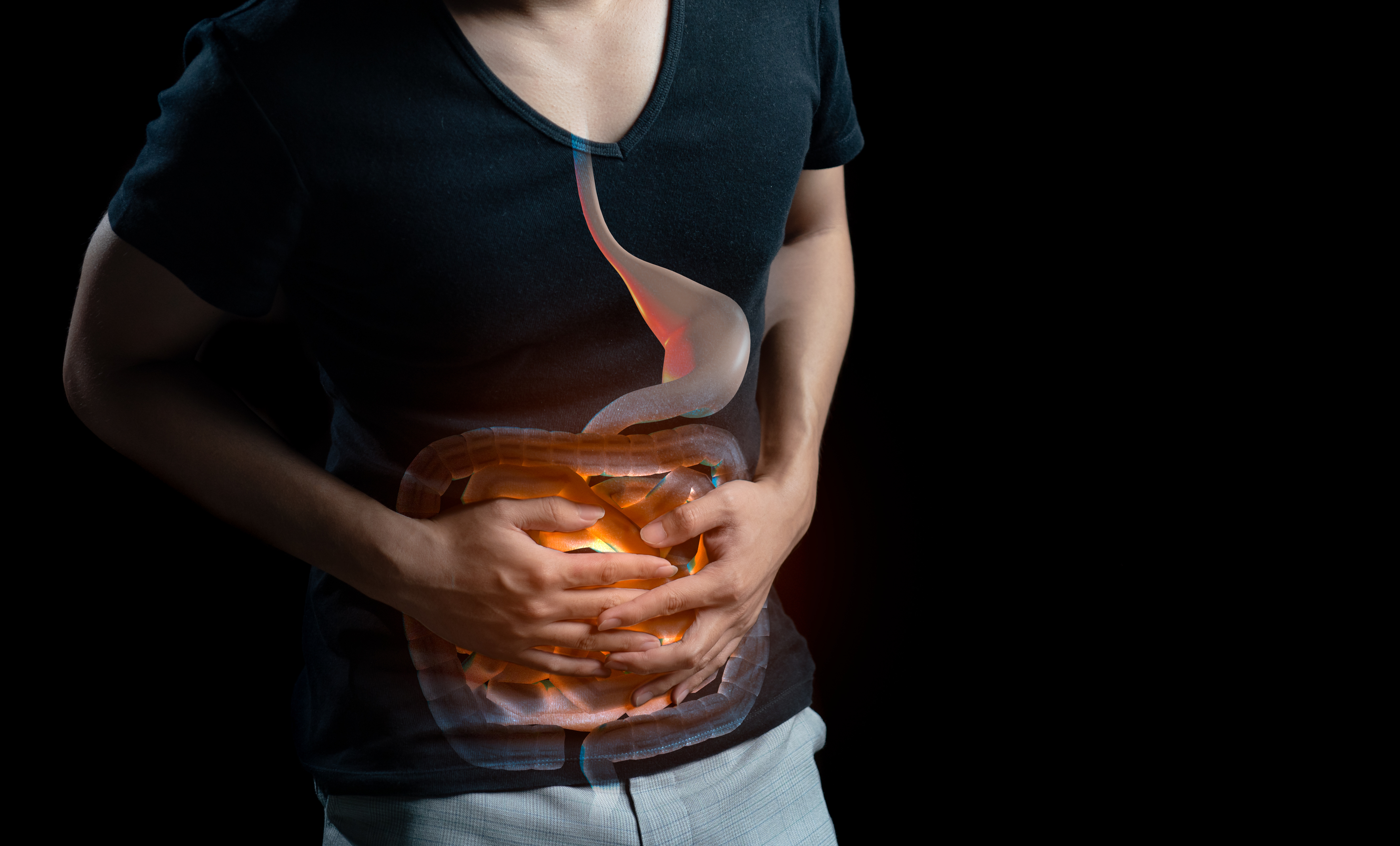
Gynecological diseases have become one of the common pathologies among women. When they develop to a certain extent, they can affect normal fertility. Therefore, it is necessary for women to pay enough attention to them. So what are the common types of gynecological diseases and their impacts?
Types of Gynecological Diseases
1. Vaginitis
The typical symptoms of vaginitis include abnormal itching in the external genital area, burning sensation, increased secretions, and odor.
Common types of vaginitis include candida vaginitis, trichomonas vaginitis, and bacterial vaginitis.
2. Cervicitis
The typical symptoms of cervicitis include increased vaginal discharge and the presence of blood streaks in the discharge.
Cervicitis can occur in women of any age, and chronic cervicitis is more common in clinical practice.
Sometimes, the irritation of the external genital secretions can also cause itching, pain in the sacral region, and lower abdominal distension.
3. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
The typical symptoms of PID include increased vaginal discharge, fever, lower abdominal pain, and sometimes nausea and fatigue.
As a common gynecological disease, delaying the treatment of PID can easily lead to chronic PID and infertility.
4. Endometritis
Patients with endometritis have increased vaginal discharge, and the discharge contains a large number of cells. After sperm enters the uterine cavity, it is affected by bacterial toxins and engulfed by white blood cells.
This can reduce the activity and quantity of sperm, resulting in a decreased chance of conception in women and, in severe cases, infertility.
In addition, women who have had endometritis may experience unstable implantation of fertilized eggs due to the influence of endometritis, which can easily lead to miscarriage.
Impacts of Gynecological Diseases
1. Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are the most common gynecological tumor in women. However, due to lack of medical knowledge, many women become very nervous and stressed when they hear that they have fibroids in their uterus.
Uterine fibroids are not actually scary. They are the most common benign tumors in the pelvic cavity of women. On average, one out of every four to five married women of childbearing age has uterine fibroids.
The severity of symptoms after being diagnosed with fibroids does not necessarily correlate with the size of the fibroids, but rather with the location of the fibroids.
For example, submucous fibroids can cause irregular vaginal bleeding at an early stage.
Even if the subserosal fibroids grow very large, they may not cause any symptoms.
Interstitial fibroids in the uterine wall can cause increased menstrual flow, longer duration, shorter intervals, and blood clots. They may even lead to anemia.
If the fibroids grow on the anterior wall of the uterus and compress the bladder, patients may also experience frequent urination and urgency.
Fibroids do not usually cause pain, but when pedunculated subserosal fibroids undergo torsion, acute abdominal pain can occur.
In addition to the above symptoms, uterine fibroids can also cause infertility.
2. Ovarian Cysts and the Risk of Malignancy
Ovarian cysts are the second most common tumors in gynecology and are prone to malignant transformation.
According to the latest epidemiological statistics, bilateral growth of malignant ovarian cysts accounts for 75%, while benign tumors account for less than 15%. Fixed location is one of their characteristics.
Functional cysts, dermoid cysts, serous cysts, and mucinous cysts usually do not cause any symptoms.
However, if the cysts become large, patients may experience mild pain or bloating in the lower abdomen.
Cysts can also compress the bladder, leading to frequent urination or difficulty urinating.
Cysts may even cause complications such as infection, torsion, bleeding, or rupture.
These symptoms can cause nausea, vomiting, fever, and severe abdominal pain, and immediate surgery is required to remove the cyst.