Many people are helpless when it comes to obesity. They not only desire to be slim and slender like thin people, but also take many practical actions in their daily lives. However, the results are often disappointing. Today, I will introduce six traditional Chinese medicine weight-loss methods that can help you unintentionally lose weight. Let's take a look at the following text!
Using traditional Chinese medicine and herbal medicine for syndrome differentiation treatment can achieve good results in reducing fat. The specific methods can be summarized as follows:
1. Stomach-Invigorating and Fat-Reducing Method
For individuals with obesity, they often experience distension and fullness in the epigastrium, belching, acid regurgitation, and foul taste in the mouth, with a greasy tongue coating. In this case, medicines such as hawthorn, barley malt, and radish seeds can be used to invigorate the stomach and aid digestion. Traditional formulas include Jiao San Xian and Bao He Wan, among others. Commercially available hawthorn fruits, hawthorn cakes, and hawthorn slices are sweet and delicious, convenient to carry around, and easy to take, but their caloric content needs to be taken into account (hawthorn cake provides approximately 177 kcal per 100 grams). Fresh radish can be eaten raw or stir-fried, and it is a simple dietary therapy for reducing fat.
2. Blood-Activating and Stasis-Dispelling Method
If an obese person has high blood lipids, it is easy to cause atherosclerosis, especially leading to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Medications that activate blood circulation and dispel stasis have effects on dilating coronary arteries, increasing blood flow, reducing blood lipids, and preventing plaque formation. For obese individuals with blood stasis and stagnation, women with amenorrhea, or the presence of purple spots on the tongue, the blood-activating and stasis-dispelling method can be used. Commonly used herbs include Chinese angelica, Chuanxiong, Salvia miltiorrhiza, Paeonia lactiflora, Millettia dielsiana, Panax notoginseng, and Typha angustifolia. Commercially available compound danshen tablets, Coronary No.1, and Coronary No.2 all have the effect of activating blood circulation, dispersing stasis, and reducing fat.
3. Expanding the Chest and Resolving Phlegm Method
Obese individuals often experience shortness of breath, chest tightness, dizziness, nausea, and a greasy tongue coating. Some people have excessive phlegm and tend to be irritable, easily getting angry, leading to elevated blood pressure, headaches, poor sleep, yellow and greasy tongue coating, and dry and hard stools. Medications such as Fructus trichosanthis are the main herbs for expanding the chest and resolving phlegm. Other herbs include Fructus aurantii, Pericarpium citri reticulatae, Pericarpium citri reticulatae viride, and Rhizoma pinelliae. Commonly used formulas include Wen Dan Tang, Gua Lou Xie Bai Tang, and Er Chen Tang.
4. Soothing the Liver and Regulating the Gallbladder Method
Soothing the liver and regulating the gallbladder is essential for liver and gallbladder diseases, especially for patients with fatty liver. Commonly used herbs include Artemisia capillaris, Curcuma aromatica, Curcuma longa, and Curcuma zedoaria. The commonly used formula is Chai Hu Shu Gan San, with modifications based on the individual's symptoms. Cassia seed can clear the liver and improve eyesight. It can be regularly brewed into tea, which has the effect of clearing liver fire and regulating blood lipids.
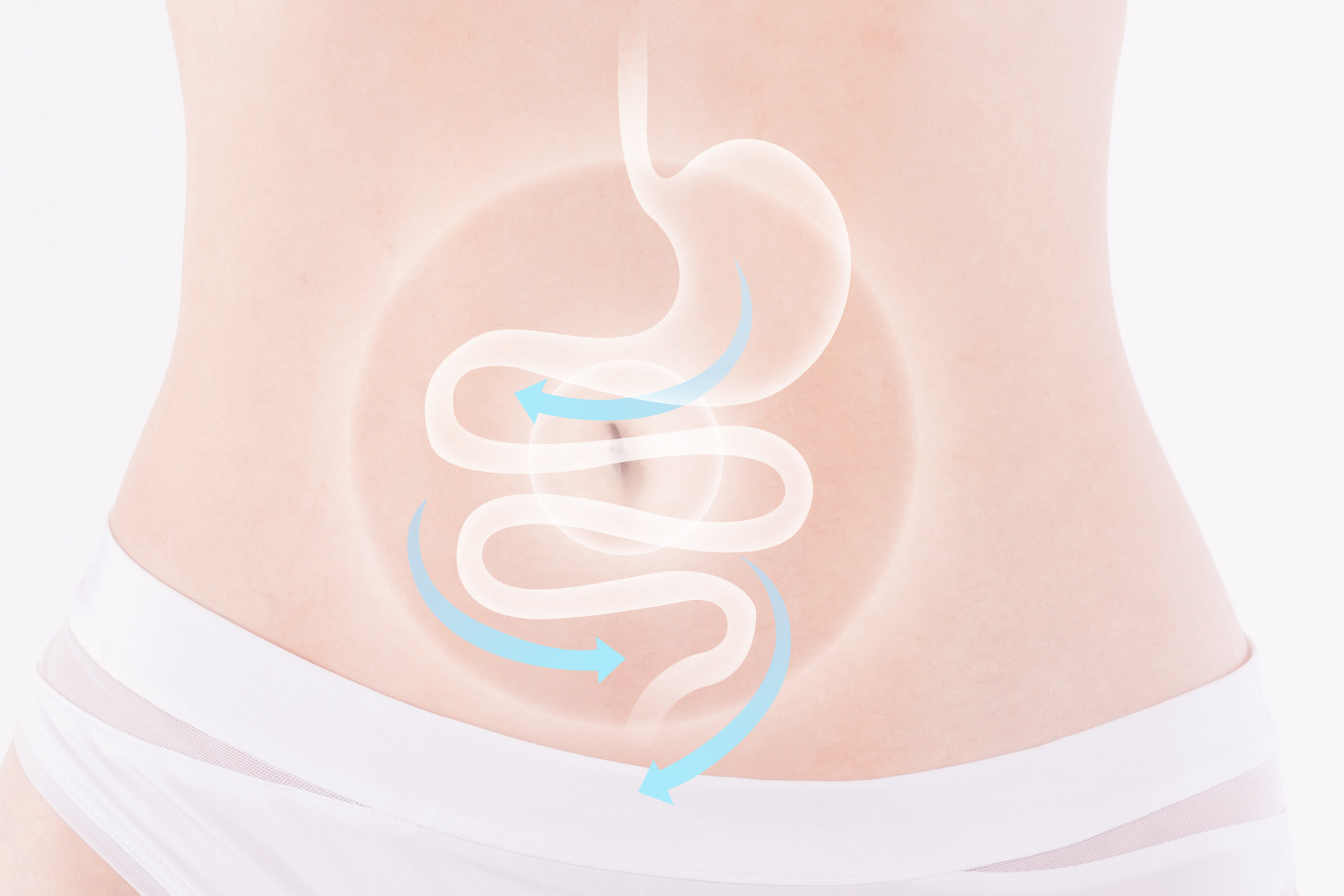
5. Diuretic and Dampness-Dispelling Method
Research has shown that diuretic and dampness-dispelling Chinese herbal medicines have the dual effect of diuresis and reducing fat. Traditional Chinese medicine literature has recorded that winter melon should be avoided by thin people, but obese people can often use winter melon seeds or winter melon rind to make soup. Alisma is a commonly used herb for diuresis and dampness-dispelling. Tea tree roots and corn silk also have diuretic effects and can be used for reducing fat. Commonly used formulas include Wu Pi Yin and Ze Xie Tang.