The triangular needle, also known as the sharp needle in ancient times, is a needle used for bloodletting. It is used to puncture certain acupoints or superficial blood vessels on the patient's body and release a small amount of blood to treat diseases. This method is called "acupuncture and bloodletting".
【Operational Method】
1. Needle
The triangular needle is generally made of stainless steel, about 6cm long. The handle of the needle is thick and cylindrical, and the body of the needle is triangular with sharp edges on three sides. Before using the needle, it should be sterilized by high-pressure sterilization or soaked in 75% alcohol for 20-30 minutes. Before the operation, disinfect the local skin with a cotton ball soaked in 2% iodine, and then remove the iodine with an alcohol cotton ball.
2. Procedures
The needling methods of the triangular needle are generally divided into puncture technique, scattered puncture technique, and picking technique.
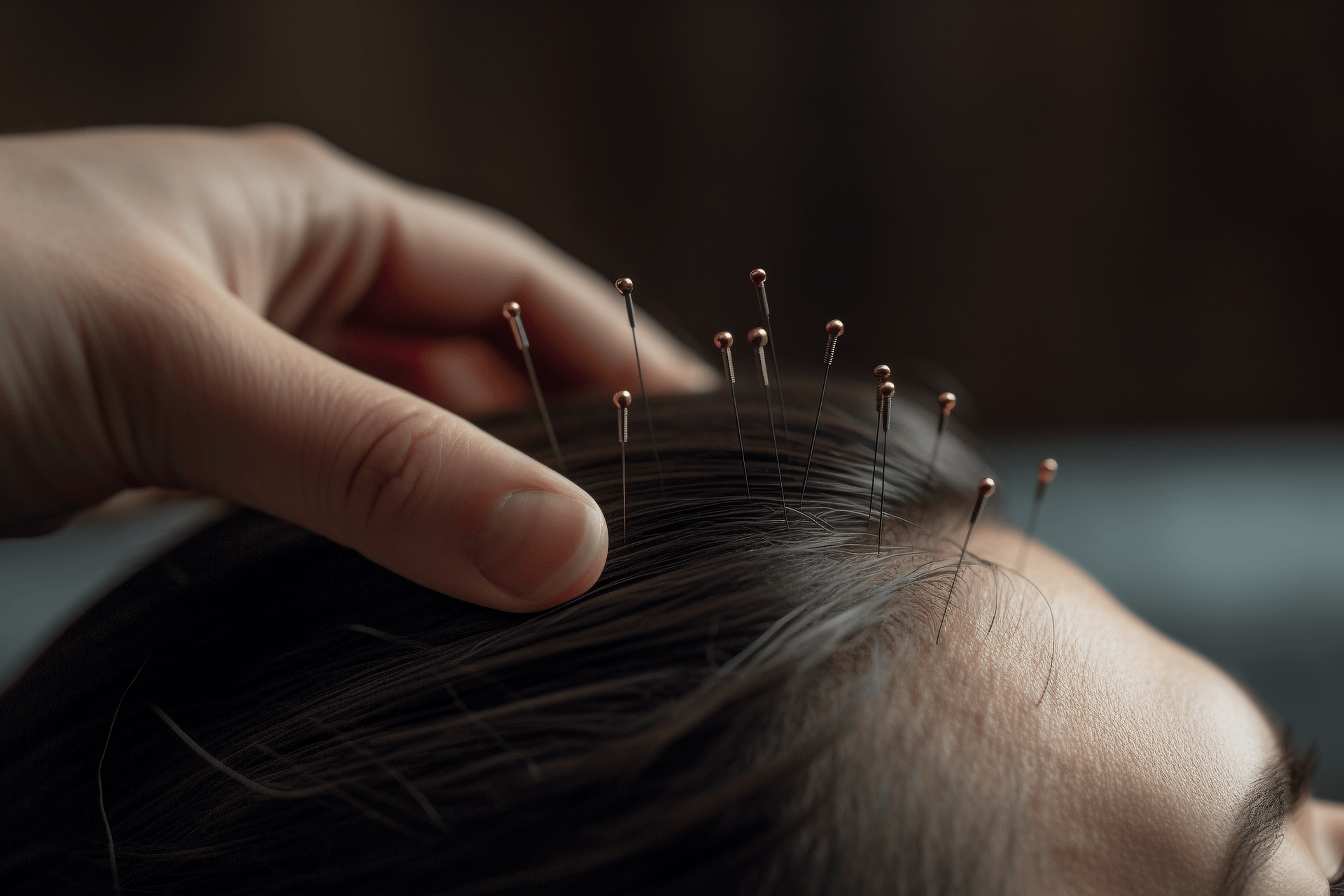
1. Puncture technique: Press the area to be needled up and down with the thumb and index finger of the left hand to make the blood accumulate in one place. Then disinfect the area. During needling, use the thumb, index, and middle fingers of the left hand to pinch the area or acupoint to be needled, hold the needle with the right hand, pinch the handle of the needle with the thumb and index finger, and place the middle finger close to the lower end of the needle body. Expose 1-2mm of the needle, aim at the sterilized area or acupoint, and insert the needle 1-2mm deep. Immediately withdraw the needle, gently squeeze the area around the needle hole with the left hand to minimize bleeding, and then press the needle hole with a disinfectant cotton ball.
2. Scattered puncture technique: Puncture multiple times around the lesion to induce bleeding. This technique is also called "surrounding puncture".
3. Picking technique: Press both sides of the needling area with the left hand to fix the skin. Hold the needle with the right hand, pick the epidermis of the acupoint or reaction point, penetrate into the skin, tilt the needle body and gently lift it to break part of the fibrous tissue. Then disinfect the area and cover it with dressing.
【Indications】
1. High fever, heatstroke, stroke, drowning, carbon monoxide poisoning, food and drug poisoning
Use puncture technique. For high fever, use the Shixuan point; for stroke, use the Hand Shier Jing point; for heatstroke, use the Chize and Weizhong points; for drowning, use the Huiyin point; for carbon monoxide poisoning, use the Taiyang point; for food and drug poisoning, use the Dazhui point.
2. Headache, stomachache, lower back pain, chest pain, flank pain, abdominal pain
For the above symptoms of excess heat, use puncture technique. For headache, use the Taiyang and Baihui points; for stomachache, use the Zusanli and Gaomang points; for lower back pain, use the Yaoyu and Weizhong points; for chest pain, use the Xinyu and Shanzhong points; for flank pain, use the Yanglingquan and Zutongyin points; for abdominal pain, use the Zusanli and Lidui points.
3. Irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea, excessive menstrual flow, stagnant labor, morning sickness, insufficient lactation
For the above symptoms of excess heat, use puncture technique. For irregular menstruation, use the Sanyinjiao and Taichong points; for dysmenorrhea, use the Taichong and Dadun points; for excessive menstrual flow, use the Zusanli and Yinbai points; for stagnant labor, use the Sanyinjiao and Zhiyin points; for morning sickness, use the Sanyinjiao and Xingjian points; for insufficient lactation, use the Zhongchong and Zusanli points.
4. Fever in children, convulsions, navel wind, vomiting and diarrhea, malnutrition
Use puncture technique. For fever in children, use the Shangyang and Guanchong points; for convulsions and navel wind, use the Renzhong and Shixuan points; for slow convulsions, use the Xingjian and Zusanli points; for vomiting and diarrhea, use the Shangyang and Gongsun points; for malnutrition, use the Sifeng and Yuzhi points.
5. Eye pain, corneal opacity, tinnitus, deafness, rhinitis, epistaxis, toothache, throat pain
For the above symptoms of excess heat, use puncture technique. For eye pain and corneal opacity, use the Taiyang, Zanzhu, and Taichong points; for tinnitus and deafness, use the Zhongzhu and Xiaxi points; for rhinitis and epistaxis, use the Yingxiang, Yintang, and Erjian points; for toothache, use the Jiache and Neiting points; for throat pain, use the Shaoshang and Neiting points. Earlobe, pinna, and tragus can also be punctured. Puncture and release blood quickly.
6. Erysipelas, abscess, stiff neck, sprains and strains
Use the surrounding puncture technique. Puncture around the affected area.
7. Hemorrhoids, cervical lymph node tuberculosis, chalazion
Use the picking technique. For hemorrhoids, pick the areas in the sacral region that are the size of grains of rice, with grayish-white, dark red, brown or light red raised papules on the skin. For cervical lymph node tuberculosis, pick the red "tuberculosis" points the size of grains of rice in the scapular region that do not fade when pressed. Pick the opposite side if the left side is affected, and vice versa. For chalazion, pick the pale red raised papules the size of grains of rice in the scapular region that do not fade when pressed. Pick the opposite side if the left eye is affected, and vice versa.
【Precautions】
1. Strict aseptic operation to prevent infection.
2. This method should not be used too frequently. Generally, it should be performed once every 2-3 days. For patients with excessive bleeding, the next treatment should be performed after 1-2 weeks.
3. This method should not be used for patients with deficiency syndrome or bleeding tendency.
4. Puncture and bloodletting should be done lightly, superficially, and quickly. Excessive bleeding should be avoided, and care should be taken not to puncture deep arteries during the operation.