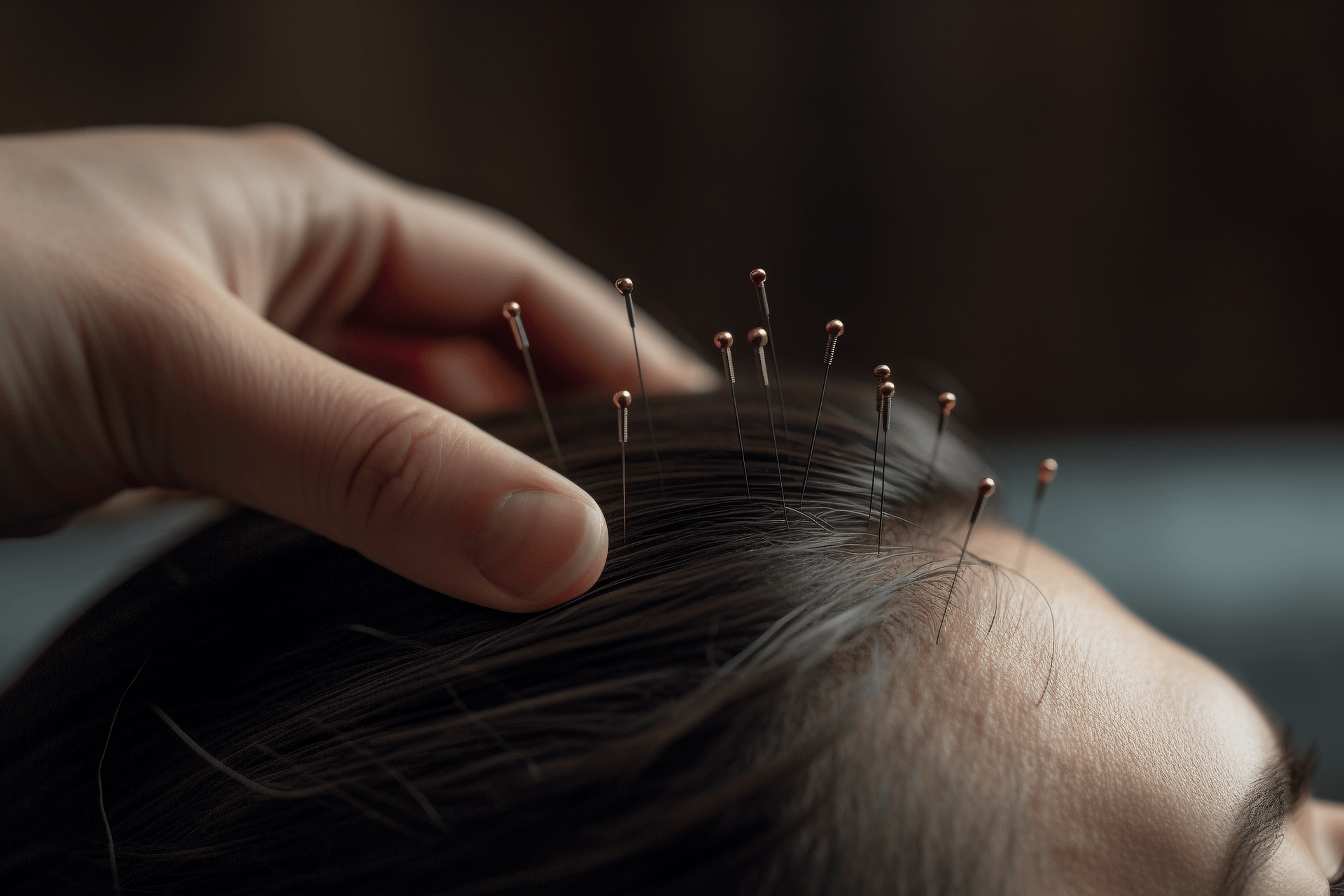
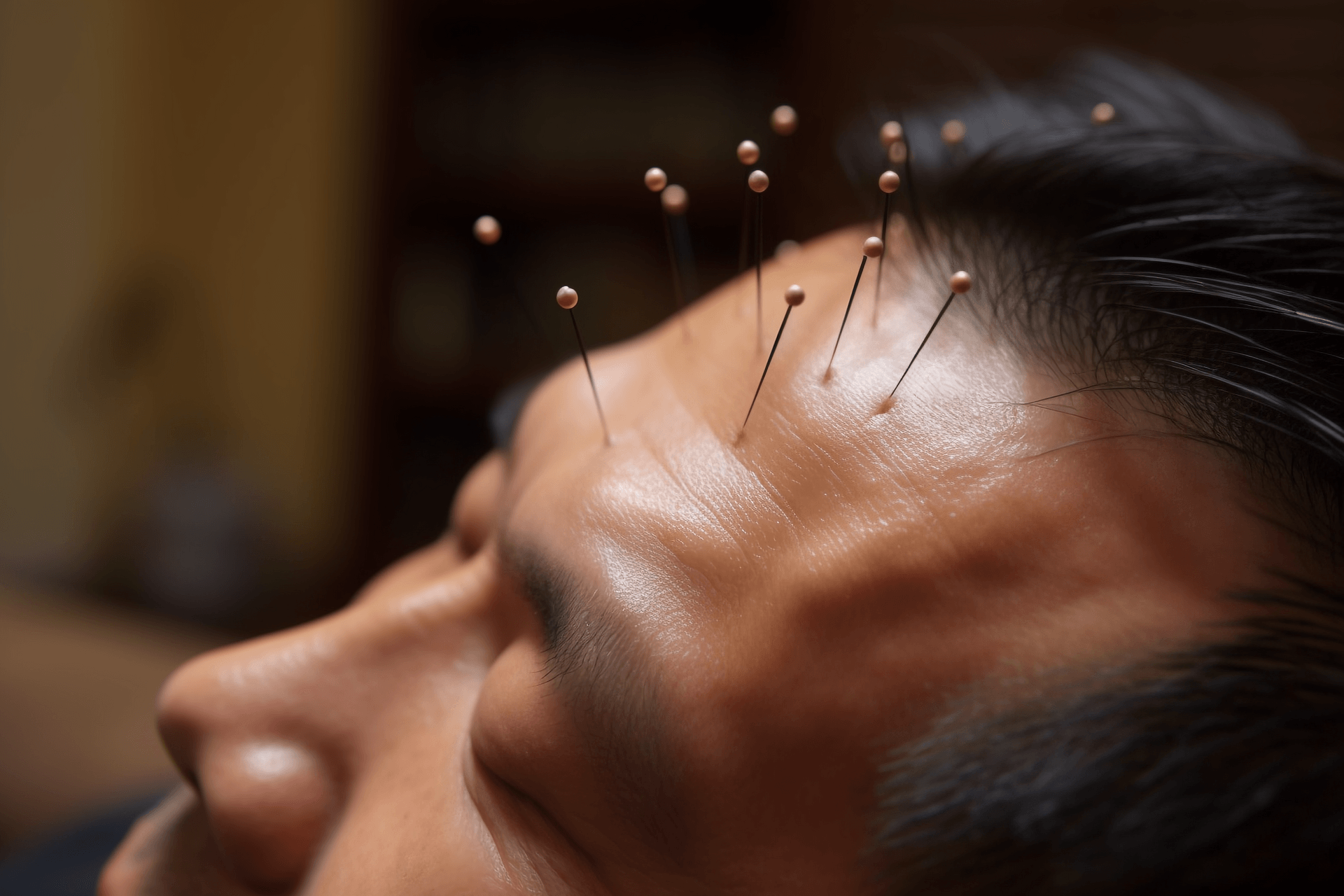
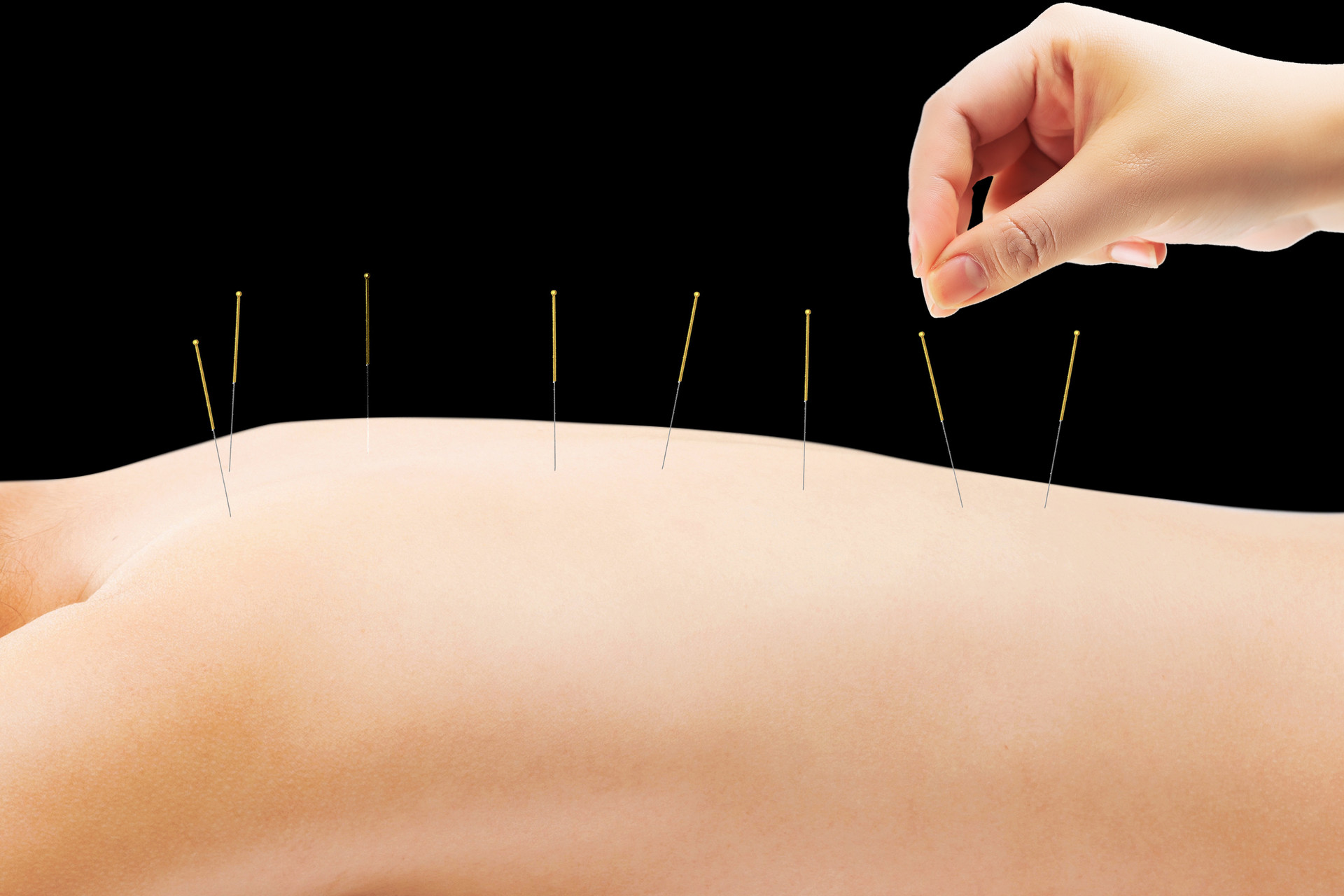
Wrist-ankle acupuncture therapy is a method of treating human diseases by needling the acupoints on the wrist and ankle. Wrist-ankle acupuncture is based on the theory of meridians and refers to modern medical neurology. The "Su Wen • Skin Theory" states: "The twelve meridians are part of the skin." The distribution areas of the twelve skin areas are based on the distribution range of the twelve meridians on the body surface. Wrist-ankle acupuncture divides the human body into six regions, which are basically consistent with the division of the twelve skin areas. For example, the Shao Yin corresponds to the 1st region on the side of the body. From here, it goes around the body from front to back, in sequence: Jue Yin, Tai Yin, Yang Ming, Shao Yang, and Tai Yang, which correspond to the division of regions 1 to 6. Upper regions 1, 2, and 3 run along the yin side, corresponding to the three yin of the hand; upper regions 4, 5, and 6 run along the yang side, corresponding to the three yang of the hand. Regions 1 to 6 correspond to the three yin and three yang of the foot. From the perspective of the relationship between the five organs, regions 1 to 6 connect the heart and lungs of the chest cavity above the diaphragm; region 6 connects the liver, spleen, and kidneys of the abdominal cavity below the diaphragm; this is consistent with the organs connected to the six meridians of the hand and foot. From the perspective of the circulation of meridians, the three yin and three yang of the hand both run through the wrist, and the three yin and three yang of the foot both run through the ankle. They also pass through specific points on the wrist and ankle, such as Houxi, Waiguan, Neiguan, Lieque, Shenmai, Zulinqi, Zhaohai, and Gongsun, which respectively connect to the Du Meridian, Yang Wei Meridian, Yin Wei Meridian, Ren Meridian, Yin Qiao Meridian, Dai Meridian, Yang Qiao Meridian, and Chong Meridian. It can be seen that the wrist and ankle are closely related to the meridians, organs, and body parts. According to the theory of specimens and root nodes, the twelve stimulation points of wrist-ankle acupuncture are all located near the wrist and ankle joints, corresponding to the local and root parts, so they can treat diseases of various body parts. The twelve stimulation points are distributed along the meridians, roughly corresponding to the positions of the twelve collaterals. Shallow needling these parts of the skin can adjust the qi of the corresponding meridians and the functions of the associated organs, in order to achieve the goal of dispelling pathogenic factors and supporting the body's normal functions.
【Operational Method】
1. Location of acupoints and their indications
1) Division of regions and indications: Wrist-ankle acupuncture divides the human body into six regions. Since the vast majority of diseases can be accurately manifested as lesions in certain parts of the body, these diseases can be classified within the range of the six longitudinal regions on both sides of the body. The regions are arranged along the longitudinal axis of the body, divided into six longitudinal regions on both sides from front to back, with the anterior and posterior midlines as the boundaries. The positions and corresponding indications of each region are as follows:
1st region: The area on both sides of the anterior midline, including the forehead, eyes, nose, tongue, trachea, lips, anterior teeth, throat, esophagus, heart, upper abdomen, umbilicus, lower abdomen, and perineum.
Indications: Frontal headaches, eye diseases, nasal congestion, drooling, toothaches, sore throat, tracheitis, stomachaches, palpitations, cowardice, enuresis, dysmenorrhea, excessive vaginal discharge, etc.
2nd region: The areas on both sides of the front of the body, including the temples, cheeks, posterior teeth, submandibular area, thyroid gland, suprasternal notch, breasts, lungs, liver, gallbladder (right), and lateral abdomen.
Indications: Temporal headaches, posterior toothaches, breast distension, chest pain, asthma, liver area pain, rib distension, etc.
3rd region: The outer edge of the front of the body, with a narrow range. It includes the vertical line along the front edge of the ear in the head and face, and the vertical line downward along the front edge of the armpit in the chest and abdomen.
Indications: Temporal superficial artery disease, chest pain or abdominal pain along the front edge of the armpit, etc.
4th region: The junction of the front and back of the body, including the area from the top of the head to the ear in a vertical line, the border of the trapezius muscle, and the vertical area from the top of the armpit to the anterior superior iliac spine in the chest and abdomen.
Indications: Headaches, tinnitus, hearing loss, temporomandibular joint disorders, chest and abdominal pain below the armpit, etc.
5th region: Both sides of the back of the body, opposite to the 2nd region in the front, including the occipital region, the outer side of the neck, and the area downward from the scapular region.
Indications: Occipital pain, stiff neck, scapular pain, lumbar transverse process syndrome.
6th region: The area on both sides of the posterior midline, opposite to the 1st region in the front, including the back of the head, the back of the neck, the spinous processes and paravertebral areas of the spine, the sacrococcygeal region, and the anus.
Indications: Posterior headaches, neck pain, acute lumbar sprain, lumbar muscle strain.
Using the xiphoid process and the junction of the rib arches on both sides as the center, draw a horizontal line around the body, representing the diaphragm. The diaphragm divides the six regions on both sides of the body into upper and lower halves. The upper half regions above the horizontal line are named upper region 1 to upper region 6, and the lower half regions below the horizontal line are named lower region 1 to lower region 6. They can also be referred to as right upper region 1 or left lower region 6, etc.
On the limbs, when the upper limbs and lower limbs are in an externally rotated position (palms facing forward), that is, the inner and outer sides of the limbs are consistent with the anterior and posterior sides of the trunk and close to the trunk, a seam appears at the place of contact. This seam represents the front midline in the front and the back midline in the back. Then, using the method of dividing the trunk, the limbs can also be divided into six regions.
2. Location of acupoints and their indications: The stimulation points of wrist-ankle acupuncture are determined based on the body area where the disease is identified within the region. The corresponding acupoints are selected on the wrist and ankle, and the same acupoints on the left and right sides should be chosen.
| 1 2 3 > >> >>|