The Back Shu Point Therapy is a method of treating systemic diseases by needling the Back Shu points on the back. The "Su Wen • Qi Fu Lun" states: "There are seventy-eight points on the foot Taiyang meridian, ... each of the Back Shu points of the five zang organs has five, and each of the Back Shu points of the six fu organs has six." This indicates that the Back Shu points are distributed along the foot Taiyang bladder meridian. The "Nei Jing" directly names the Back Shu points after the zang-fu organs, indicating their special relationship with the zang-fu organs and meridians. The foot Taiyang bladder meridian ascends to the head and connects with the brain, the bladder belongs to the kidney, and it directly meets the Du meridian at the top of the head and the Feng Fu point. Through its relationship with the foot Shaoyin meridian and the meeting of the Du meridian with the hand and foot Yangming meridians, it determines its special status as "belonging to the yang meridians," and the Back Shu points are closely related to the zang-fu organs because of this. The "Ling Shu • Wei Qi" states: "The foot Shaoyin ... are located at the Back Shu and under the tongue meridians; the foot Jueyin is located at the Back Shu; the hand Shaoyin is located at the Back Shu." This means that the back is the place where the qi of the zang-fu meridians is transported, so needling the Back Shu points can regulate the qi of the zang-fu meridians to achieve the purpose of treating systemic diseases.
[Operating Methods]
1. Location of the acupoints
The Back Shu points are all located on the 1st lateral line of the foot Taiyang bladder meridian on the back and waist, which is 1.5 cun away from the midline of the back. Generally, they are arranged according to the position of the zang-fu organs and named after them. The Lung Shu, Jueyin Shu, Heart Shu, Liver Shu, Gallbladder Shu, Spleen Shu, and Stomach Shu points are located 1.5 cun away from the lower edge of the 3rd, 4th, 5th, 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th thoracic vertebrae spinous processes respectively; the Sanjiao Shu and Kidney Shu points are located 1.5 cun away from the lower edge of the 1st and 2nd lumbar vertebrae spinous processes respectively; the Large Intestine Shu point is located 1.5 cun away from the lower edge of the 4th lumbar vertebrae spinous process; the Small Intestine Shu and Bladder Shu points are located 1.5 cun away from the lower edge of the 1st and 2nd sacral vertebrae spinous processes respectively, totaling 12 points.
2. Principles and methods of point selection
1. Select points corresponding to the affected area: Each Back Shu point is associated with specific diseases. When a disease occurs in a certain area, select the corresponding Back Shu point. For example, for enteritis, select the Large Intestine Shu point; for stomach pain, select the Stomach Shu point, and so on.
2. Select points based on the theory of zang-fu organs: For example, select the Lung Shu point for skin diseases, as the lungs govern the skin and hair.
3. Select points based on the relationship between the exterior and interior meridians: For example, for tongue sores caused by excessive heart fire, the Heart Shu point can be paired with the Small Intestine Shu point.
4. Select points based on the combination of Back Shu and Mu points: The Back Shu points are specific points where the qi of the zang-fu meridians is transported on the back, while the Mu points are specific points where the qi of the zang-fu meridians converges in the chest and abdomen, with one Mu point for each of the twelve meridians. When they are paired, they have good therapeutic effects. For example, the Kidney Shu point can be paired with the Jingmen point to treat edema, kidney deficiency, lumbago, enuresis, nocturnal emission, and other conditions.
5. Select points based on the combination of Back Shu and Yuan points: The Yuan points are the specific points where the original qi of the zang-fu organs passes through and stays, with one Yuan point for each of the twelve meridians. For example, the Heart Shu point can be paired with the Shenmen point to treat chest pain, palpitations, dizziness, insomnia, and other conditions.
3. Procedure
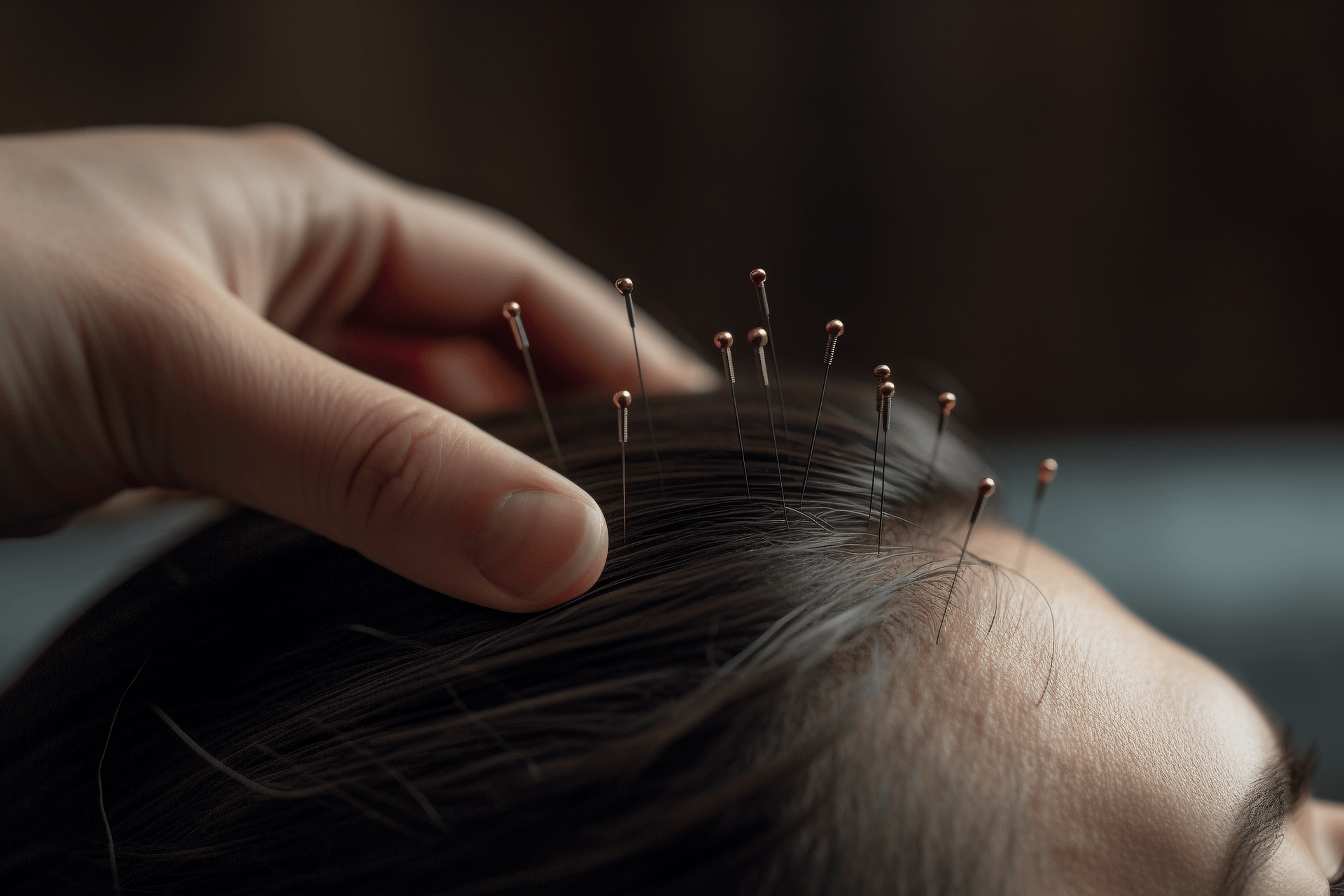
Conventional disinfection, use a 30-32 gauge, 3.3cm (1 inch) filiform needle, gently insert the needle, with a depth of about 0.5-0.8 inches. The main technique is twisting. Leave the needle in for 15 minutes after obtaining qi. Depending on the condition, some may not leave the needle in.
[Indications]
This therapy has a wide range of indications, especially for the treatment of visceral diseases, such as cough, asthma, palpitations, chest pain, lumbago, impotence, premature ejaculation, enuresis, nocturnal emission, insomnia, and other conditions. For point selection, please refer to the body acupuncture therapy.
[Precautions]
Do not needle the Back Shu points too deeply to avoid damaging the internal organs, especially for patients with lung emphysema and enlarged liver and spleen, extra attention should be paid. The practitioner needs to be highly focused during needling, and the patient's position should be moderate, with a strict control of the needle insertion angle. If the back is needled too deeply and the lungs are injured, it can cause traumatic pneumothorax. Mild symptoms include chest pain, chest tightness, palpitations, and difficulty breathing, while severe symptoms include difficulty breathing, cyanosis of the lips and nails, sweating, low blood pressure, and even shock. Prompt first aid measures should be taken in such cases.