A method for treating diseases. The spine is closely connected to the meridians. The foot Taiyang meridian "surrounds the spine"; the foot Shaoyin meridian "pierces the spine"; the foot Yangming meridian tendons "ascend and connect to the ribs and belong to the spine"; the Du meridian "surrounds the spine" and "pierces the spine", intersecting with the other yang meridians. The spine is related to the five Zang organs and the six Fu organs through the meridian system. Acupuncture on the spine can regulate the Qi and blood of the whole body's internal organs to treat diseases.
[Operational Method]
1. Acupoint location
The acupoints on the spine are located on both sides below the spinous process of the vertebrae, distributed in the cervical vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae, lumbar vertebrae, and sacral vertebrae.
1. Cervical Spine: Cervical spine acupoints 1-3 are located 0.5 cun away from the side below the spinous process of the 4th, 5th, and 6th cervical vertebrae. There are 3 acupoints on each side, totaling 6 acupoints on both sides.
2. Thoracic Spine: Thoracic spine acupoints 1-12 are located 0.5 cun away from the side below the spinous process of the 1st to 12th thoracic vertebrae. There are 12 acupoints on each side, totaling 24 acupoints on both sides.
3. Lumbar Spine: Lumbar spine acupoints 1-5 are located 0.5 cun away from the side below the spinous process of the 1st to 5th lumbar vertebrae. There are 5 acupoints on each side, totaling 10 acupoints on both sides.
4. Sacral Spine: Sacral spine acupoint is located 0.5 cun away from the side below the 1st sacral vertebrae spinous process (pseudo spinous process).
2. Acupoint selection principles
1. Select acupoints based on the symptoms. Choose the corresponding acupoints according to different symptoms and the main treatment of the acupoints. For example, select thoracic 11, 12, and lumbar 1 for diarrhea and abdominal pain.
2. Select acupoints based on tenderness points. Use pushing method and pressing method to check for tenderness points. There is a certain regularity between the tenderness points of diseases and the selection of acupoints, as described below:
(1) Respiratory system: Thoracic vertebrae 1-5.
(2) Circulatory system: Thoracic vertebrae 5-8.
(3) Digestive system: Thoracic vertebrae 5-12.
(4) Nervous system: Cervical vertebrae 4-6, Thoracic vertebrae 6-8.
(5) Musculoskeletal system: (upper limbs) Thoracic vertebrae 1-3; (lower limbs) Lumbar vertebrae 1-5.
(6) Metabolic system: Thoracic vertebrae 8-9, Lumbar vertebrae 1-4.
(7) Endocrine system: Cervical vertebrae 4-6, Thoracic vertebrae 3-5.
(8) Ophthalmic disorders: Cervical vertebrae 4-6.
(9) Genitourinary system: Lumbar vertebrae 1-5, Sacral vertebra 1.
(10) Obstetrics and lactation: Thoracic vertebrae 6-7.
3. Procedure
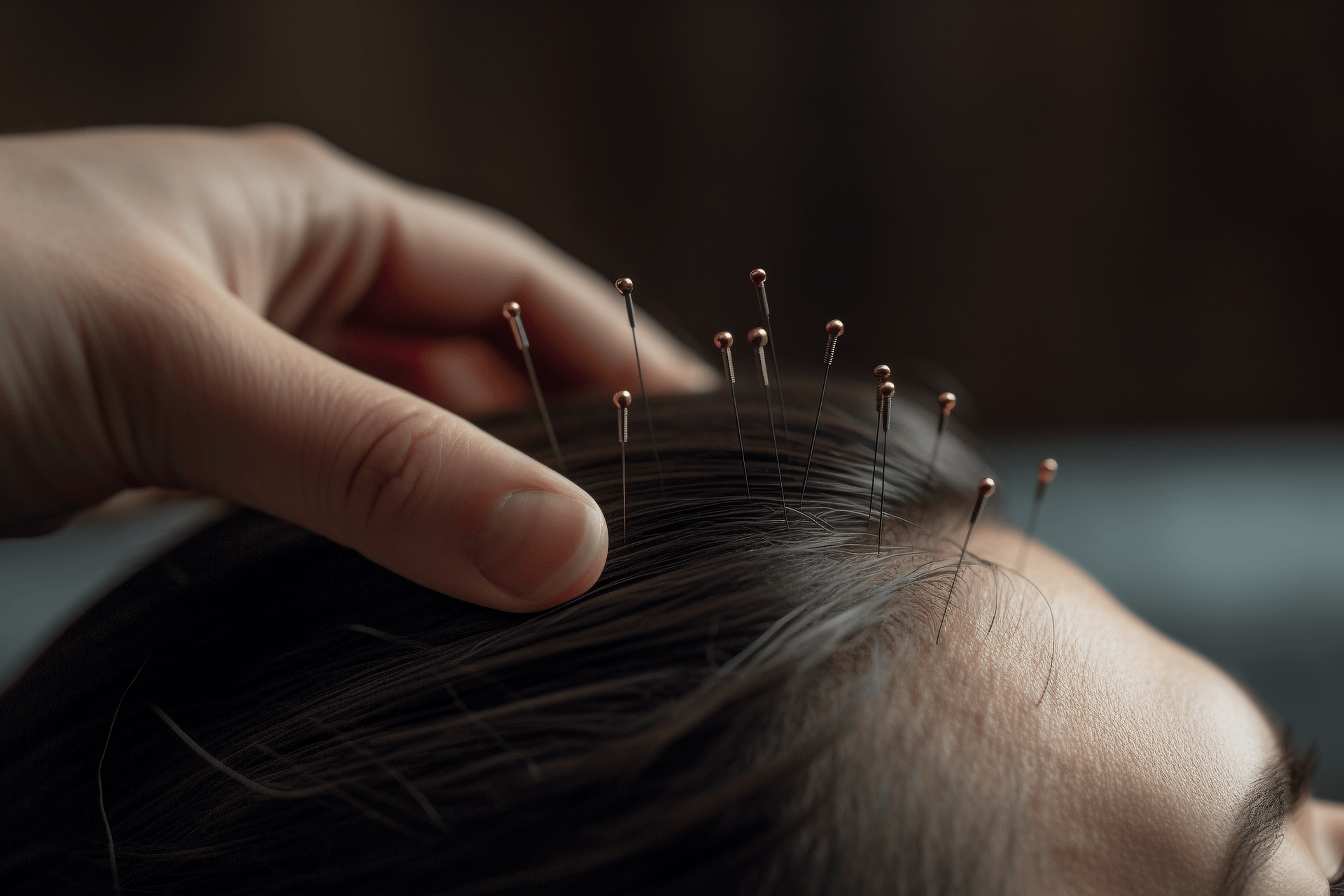
The patient lies prone, routine disinfection is done, and the operator holds a 5cm (1.5-inch) long filiform needle at a 75-degree angle to the vertebrae (with the needle tip facing the spine). The needle is inserted below the vertebrae, about 1 inch deep depending on the patient's body size. The needle is twisted and rotated to make the needle sensation transmit along the intercostal space or the spine. If there is no transmission sensation, the direction of needle insertion can be adjusted, and the technique can be repeated. The needle is left in place for 30 minutes.
[Mainly Treat Diseases]
1. Bronchitis, asthma
Treat with spinal needling therapy. Use thoracic 6, and pair it with thoracic 3 and 5.
2. Gastritis, gastric ulcer, gastric spasms
Treat with spinal needling therapy. Use thoracic 6, and pair it with thoracic 12.
3. Diabetes, diabetes insipidus, prostatitis, enuresis, spermatorrhea, impotence, amenorrhea
Treat with spinal needling therapy. Use thoracic 6, and pair it with lumbar 1 and 4.
4. Stroke hemiplegia, paralysis from trauma, sequelae of infantile paralysis
Treat with spinal needling therapy. Use thoracic 6, and pair it with thoracic 5, lumbar 4, and sacral 3.
【Precautions】
Strictly control the depth and angle of needle insertion to avoid damaging internal organs and causing traumatic pneumothorax.