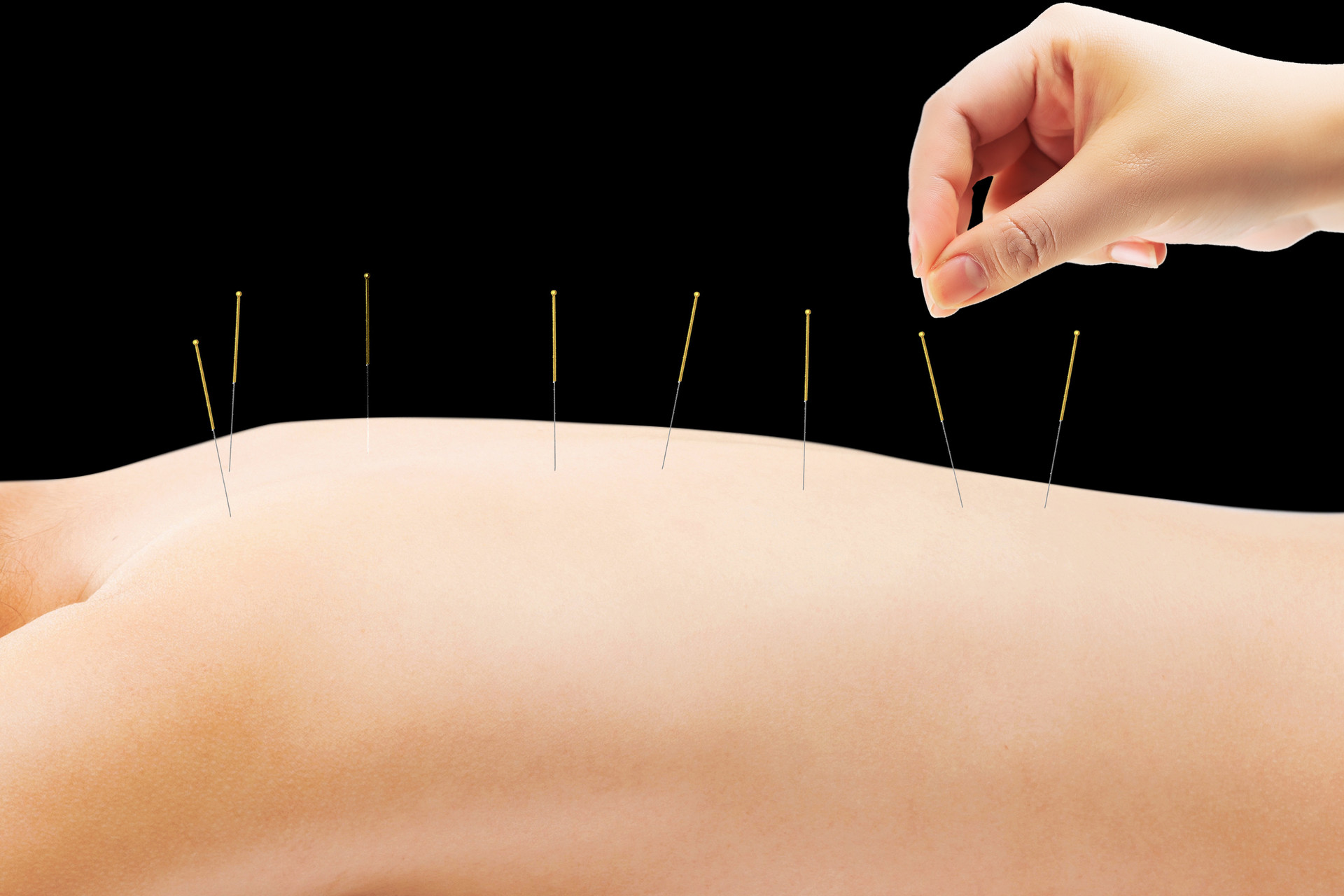
Overview
Abdominal acupuncture is a method of treating diseases by stimulating acupoints on the abdomen to regulate the dysfunction of internal organs. The treatment generally uses a comprehensive approach to selecting acupoints, including acupoints along the meridians, specific locations, and the Eight-Sided Acupoint Selection method. The selection of acupoints and the technique of needle insertion are based on the patient's condition and treatment plan.
Procedure
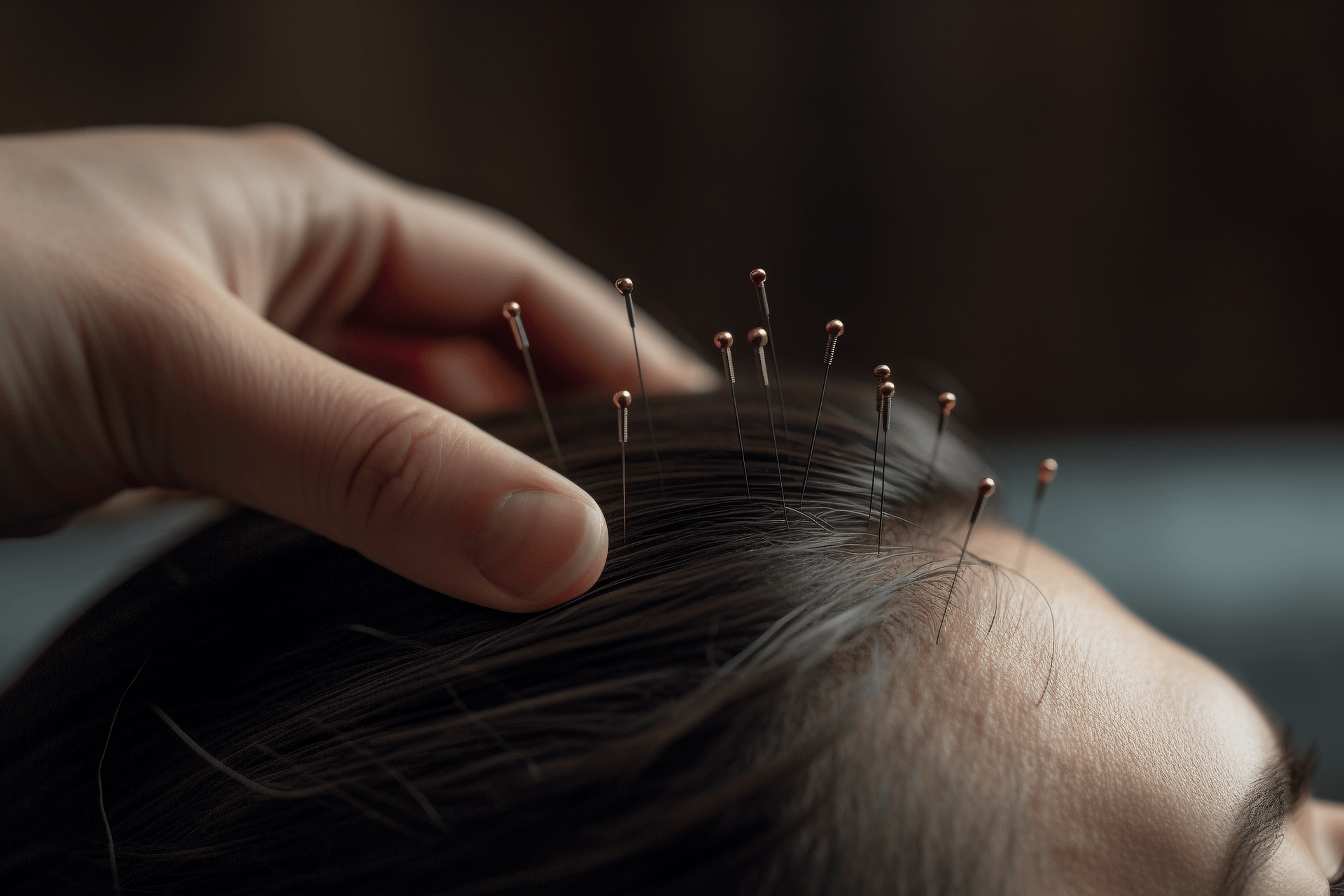
Abdominal acupuncture should be performed using uniform-length filiform needles to facilitate the observation of different depths of needle insertion. The length of the needle should be chosen according to the thickness of the patient's abdominal wall. The technique should be gentle and slow, using either a twisting motion without lifting or a slow lifting motion.
Specialized abdominal acupuncture therapy follows a strict order of needle insertion. During the treatment, it is necessary to first stimulate acupoints that regulate the function of internal organs, then acupoints that open the meridians, and finally acupoints at specific locations to adjust local qi.

Illustration of Abdominal Acupuncture Procedure
Indications
Abdominal acupuncture has a wide range of indications, primarily for the treatment of internal diseases, chronic and difficult-to-treat diseases, and long-term illnesses.
(1) Short-term diseases caused by insufficient qi of internal organs, such as frozen shoulder, cervical spondylosis, lumbar spondylosis, osteoarthritis, lower back and leg pain, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, etc.
(2) Systemic diseases caused by internal organ damage over a long period of time, such as cerebral arteriosclerosis, cerebrovascular diseases and their sequelae, coronary atherosclerotic heart disease, diabetes, etc.
(3) Common diseases in various clinical departments, such as gynecological infections, urinary tract infections, prostatitis, urticaria, allergic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, etc.
(4) Diseases caused by endocrine disorders, such as prostatic hyperplasia, female breast hyperplasia, ovarian cysts, sexual dysfunction, postoperative pain relief for thrombosed hemorrhoids, functional recovery after bone fracture fixation, etc.
(5) Difficult-to-treat diseases, such as postpartum wind, pulmonary fibrosis, etc.
(6) Other diseases with unsatisfactory results from various acupuncture treatments.
Precautions
(1) Due to the needle insertion in the abdomen, abdominal acupuncture is contraindicated for acute abdominal conditions with unknown causes, acute peritonitis, acute appendicitis, abdominal varices caused by liver or spleen enlargement, and during mid to late pregnancy.
(2) Caution should be exercised when treating patients with chronic diseases and weak constitution.
(3) For patients with liver or spleen enlargement, avoid deep needle insertion in the lower ribs to prevent organ injury.
(4) Deep needle insertion in abdominal acupuncture should not be too deep.
Special Acupoints
Jinhe - Located in the lower abdomen, 0.5 cun beside Qihai acupoint.
Indications: inguinal hernia in children, lower back pain, lumbar muscle strain, weakness in the lower limbs, and endocrine disorders.
Shangfengshi - Located in the upper abdomen, 1.5 cun above the navel, 2.5 cun lateral to the anterior midline (0.5 cun beside Shuimumen, 0.5 cun above).
Indications: elbow joint pain, numbness in the elbow and arm, difficulty in flexing and extending the elbow.
Shangfengshi Outer - Located in the upper abdomen, 1 cun above the navel, 3 cun lateral to the anterior midline (3 cun beside Shuimumen or 0.5 cun outside and 0.5 cun below Shangfengshi).
Indications: wrist joint pain, finger joint pain, restricted movement, numbness.
Xiafengshi - Located in the lower abdomen, 1.5 cun below the navel, 2.5 cun lateral to the anterior midline (2.5 cun beside Qihai or 0.5 cun outside and 0.5 cun below Wailin).
Indications: knee joint pain, restricted movement of the knee joint.
Xiafengshi Lower - Located in the lower abdomen, 2 cun below the navel, 3 cun lateral to the anterior midline (3 cun beside Shimen or 0.5 cun outside and 0.5 cun below Xiafengshi).
Indications: pain on the outer side of the lower leg, restricted movement, ankle joint pain, numbness.
Expert Experience
Shangfengshi and Xiafengshi are new acupoints in the abdominal acupuncture system.
Both Shangfengshi points correspond to the liver and spleen, with the left side mainly regulating the spleen and the right side mainly regulating the liver. These acupoints are located along the pathway of the foot jueyin liver meridian. Deep needle insertion can regulate the qi of the liver and spleen, promoting liver health, and harmonizing qi and stomach. They are used in the clinical treatment of liver qi stagnation and chest and rib pain, liver depression and insomnia, bitter taste and acid reflux, headache, and hearing loss caused by liver fire.
The two Xiafengshi points have different functions. The left Xiafengshi point mainly regulates the large intestine, which is closely related to the lungs. Deep needle insertion can clear the large intestine and descend lung qi, used for lung qi congestion, coughing, and constipation. The right Xiafengshi point mainly regulates the small intestine, which is closely related to the heart. Deep needle insertion can clear heart and liver heat, used for excessive heart and liver fire, irritability, red tongue tip, and hot urine.
Proper application of the dispersing and draining effects of the Fengshi points is essential, especially for the two Xiafengshi points. They should not be used indiscriminately in patients with weak constitution and deficiency of qi and yang. If diarrhea occurs, timely tonification of Guanyuan and Qihai points should be performed to strengthen yang qi.