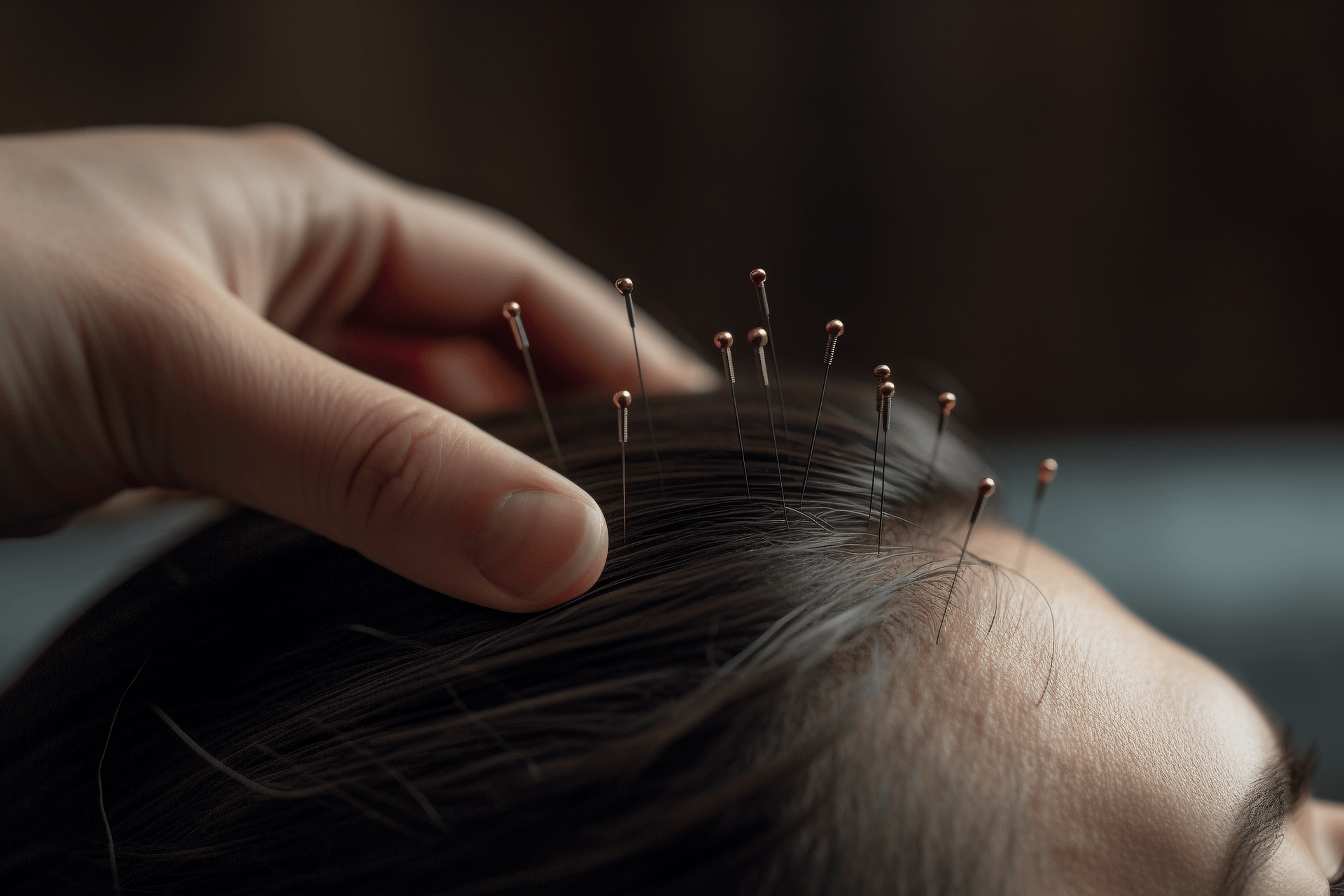
The water needle method, also known as "acupoint injection method," is a method of treating diseases by injecting Chinese and Western medicine into acupuncture points. It combines needle insertion with medication, adjusting the function of the viscera and blood through acupoint injection, and changing the imbalance of yin and yang to achieve the goal of treating diseases.
【Procedure】
1. Tools and Medication
- Sterilized syringes and needles. Commonly used syringes are 1ml, 2ml, 5ml, 10ml, and 20ml; commonly used needles are 4-6 gauge regular injection needles, dental 5 gauge long needles, and long needles for closed use, etc.
- Medication suitable for intramuscular injection according to the needs of different diseases. Commonly used medications include Danshen, Danggui, Chuanxiong, Safflower, Banlangen, Weilingxian, Xuchangqing, Xiatianwu, Zhongjiefeng, Dinggongteng, Yuxingcao, Dilong, Yinhuan, etc. Injection liquids such as Vitamin B1, B6, B12; Compound Vitamin B injection; Vitamin C, Vitamin D3 Calcium Gelatin injection; Glucose solution, physiological saline, procaine hydrochloride, placental tissue fluid, injection water, etc.
2. Procedure
- Injection sites:
1) Select the appropriate main acupoints according to the prescription principles of general acupuncture treatment for different diseases.
2) For the chest, abdomen, waist, and back, acupoints with obvious positive reactions during palpation can be selected.
3) Positive reaction points that are felt along the distribution of meridians or as tender points, cord-like or nodular.
4) For soft tissue injuries, select the most obvious tender points; for muscle belly or tendon injuries in longer muscles, select the starting and ending points of the muscle belly; for lumbar disc herniation, inject the medication around the spinal nerve root.
- Procedure and dosage:
1) First, select the appropriate syringe and needle according to the selected acupoints and dosage of medication. After local skin disinfection, use a rapid needle insertion technique to puncture the subcutaneous tissue, then slowly advance or move the needle up and down until a "qi" sensation of sourness, distension, sinking, or heaviness is felt. Withdraw the needle slightly to check for blood return. If there is no blood return, the medication can be injected. Generally, medium speed is used for injection in common diseases; for weak patients with chronic diseases, the medication is slowly pushed in with gentle stimulation; for strong patients with acute diseases, the medication is quickly pushed in with strong stimulation. If a larger volume of medication needs to be injected, the needle can be gradually pulled out from the deep layer to the superficial layer while pushing the medication, or the direction of the injection needle can be changed to push the medication.
2) Injection depth: Determine the angle and depth of needle insertion based on the location of the acupoint and the requirements of the diseased tissue. Generally, if there is pain with light pressure, the lesion is mostly in the superficial layer, so the injection should be shallow; if pain is only felt with strong pressure, the lesion is mostly in the deep layer, so the injection should be deep.
3) Medication dosage: For the head, face, and ear acupoints, a smaller dosage should be used, with each acupoint receiving an injection of 0.1-0.5ml. For the limbs and areas with thick muscles in the waist and back, a larger dosage should be used, with each acupoint receiving an injection of 2-5ml. Less irritating medications require larger doses, while more irritating medications require smaller doses. For small dosage acupoint injections, the medication dosage can be reduced to 1/10-1/3 of the general dosage. The common dosage for Chinese medicine injections is 1-2ml.
- Treatment course: Inject once daily or every other day, or once every 2-3 days for stronger reactions. Alternate between acupoints on the left and right sides. Generally, 10 injections make up one course of treatment. Rest for 5-7 days before starting the next course.
【Indications】
1. Brachial plexus injury, axillary nerve injury, musculocutaneous nerve injury, median nerve injury, radial nerve injury, ulnar nerve injury, sciatic nerve injury, gluteal nerve injury, saphenous nerve injury, peroneal nerve injury, shinbone nerve injury.
- Commonly used acupoints for upper limbs: Jianzhen, Jianqi, Bifu, Xiabai, Chize, Quchi, Shousanli, Shaohai, Xiaohai, Waiguan, Neiguan, Hegu, Houxi. Commonly used acupoints for lower limbs: Huantiao, Zhibian, Yinmen, Biguan, Futu, Liangqiu, Yanglingquan, Yinlingquan, Fenglong, Chengshan, Juegu, Taixi.
- Medication: Vitamin D1 or Vitamin B12.
2. Sequelae of cerebral palsy, flaccidity syndrome.
- For sequelae of cerebral palsy, select the motor and sensory areas of the head; for flaccidity syndrome, select Biguan, Futu, Zusanli.
- Medication: 10% Danggui liquid, 10% Safflower liquid.
3. Cervical spondylosis, costochondritis, intercostal neuralgia, sciatica.
- For cervical spondylosis, select Fengchi, Jianzhen, Quchi, Shousanli, Hegu; for costochondritis, select Ashi; for intercostal neuralgia, select Zigou, Yanglingquan; for sciatica, select Ashi.
- Medication: 5% Danggui liquid, 10% Jiuxueteng liquid, 5% Safflower liquid, Vitamin B1.
4. Hiccup, gastric prolapse.
- For hiccup, select Neiguan, Zusanli; for gastric prolapse, select Zhongwan, Zusanli.
- Medication: Injection water.
5. Asthma, chronic bronchitis.
- For asthma, select Dingchuan; for chronic bronchitis, select Feishu, Lieque, Fenglong.
- Medication: Vitamin B1, 5% Danggui liquid, 10% Safflower liquid.