Overview
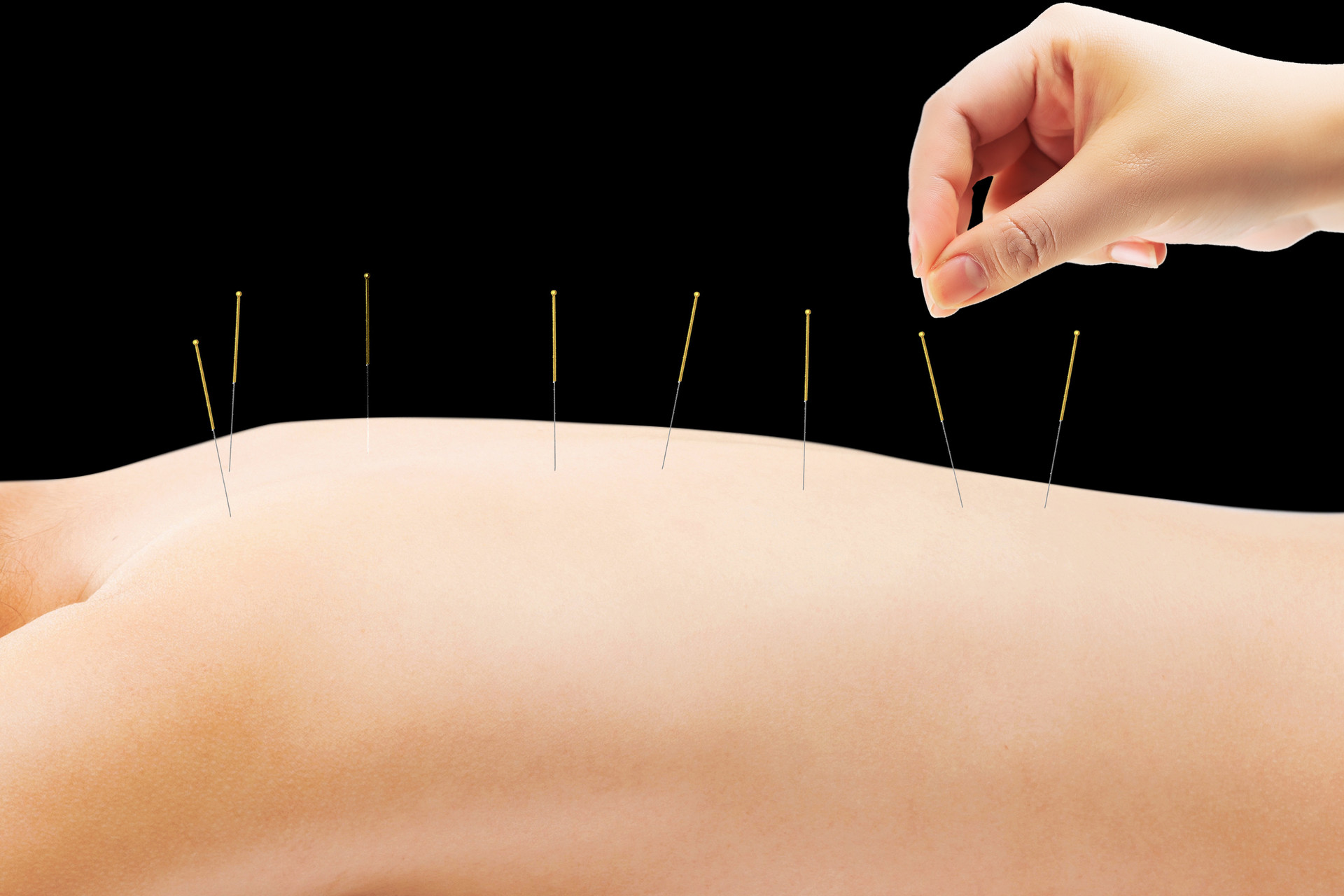
Ear acupuncture is a method of using fine needles or other techniques to stimulate ear acupoints for the prevention and treatment of diseases. In clinical practice, the shape and color changes of ear acupoints, as well as pathological reactions, have certain reference significance for disease diagnosis.
It mainly includes more than ten stimulation methods such as fine needle, embedded needle, electroacupuncture, adhesive pressure, medication injection, ear cutting and medication application, adhesive plaster, ear acupuncture, bloodletting, magnetic therapy, massage, and laser.
Procedure
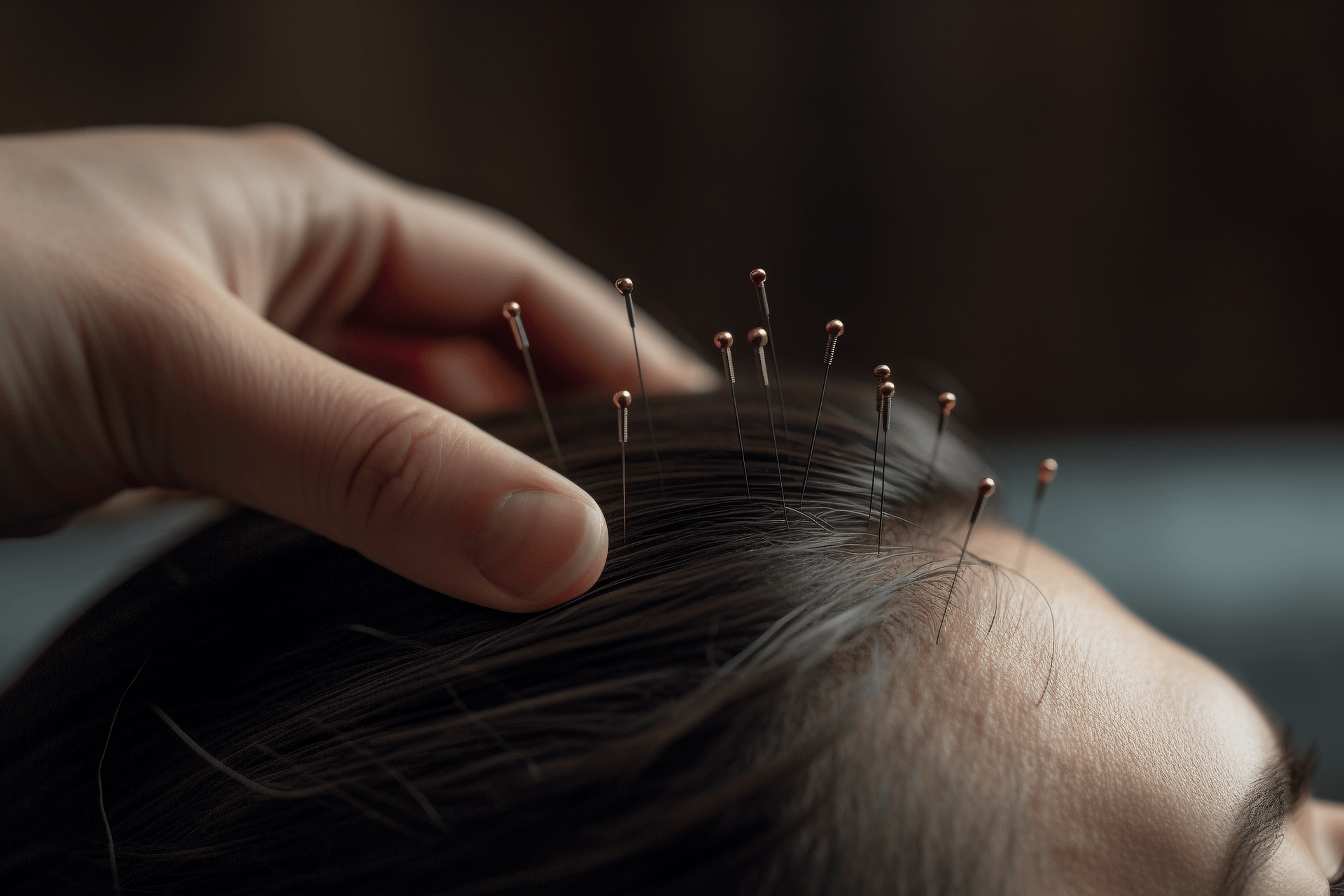
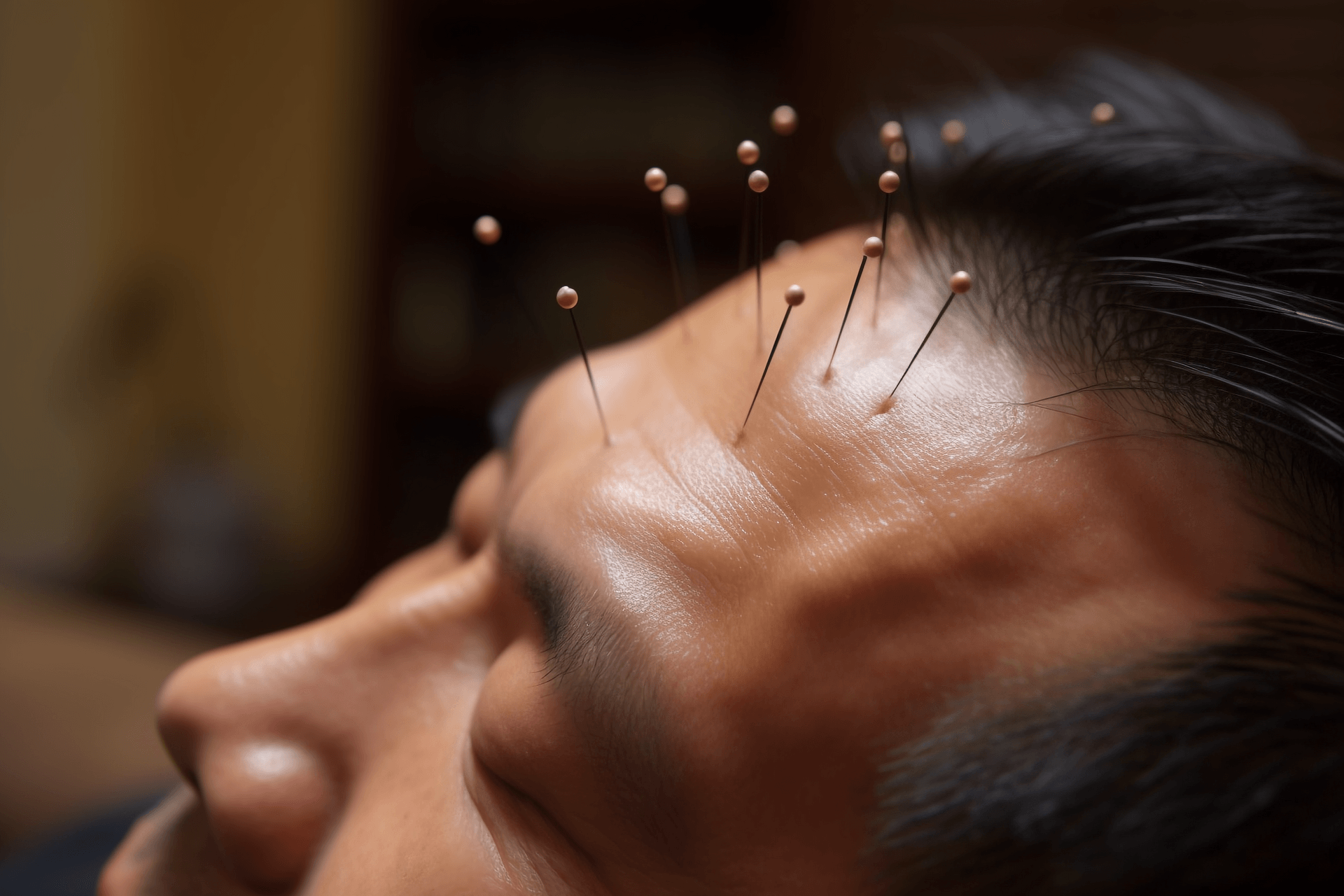
(1) Fine Needle Technique
Before needling, disinfect with 75% alcohol. The doctor holds the back of the ear where the needle will be inserted and fixes the auricle to control the depth of needling and reduce pain. The other hand holds the needle and inserts it into the stimulation point.
After the needle is inserted into the ear acupoint, if there is a strong local sensation, the patient's symptoms often immediately alleviate. If there is no needle sensation locally, the direction, depth, and angle of needling should be adjusted. The intensity and technique of stimulation should be considered based on the patient's condition, physique, syndrome, and tolerance.
The needle is generally left in place for about 15-30 minutes. For chronic diseases and painful conditions, the needle can be left in place for a longer time. For severe pain, the needle can be left in place for 1-3 hours or even longer.




Illustration of the Fine Needle Technique
(2) Bloodletting Technique
This method uses triangular needles or surgical blades to puncture the skin of the auricle for the treatment of diseases such as fever, inflammation, and hypertension.
The procedure is as follows: massage the auricle to congest it, disinfect it, fix the auricle with the left hand, use the right hand to quickly puncture the ear acupoint with a dotting technique, immediately squeeze the ear with two fingers to make it bleed 3-5 drops, and then use a sterilized cotton ball to wipe and press to stop bleeding. Acute conditions can be treated 1-2 times a day, while chronic conditions can be treated every other day.
(3) Pellet Pressure Technique
This is a simple alternative to embedded needle therapy, where small particles of medication are applied and pressed onto the surface of the ear acupoint with adhesive tape. This technique provides continuous stimulation to the acupoint, is safe, painless, and has minimal side effects. It is widely used in clinical practice.
For this technique, Wang Bu Liu Xing Zi is often used as the pellet pressure material because of its smooth surface, appropriate size, and hardness. Before use, it is boiled in hot water for 2 minutes, dried, and stored in a bottle. The intensity of pressure in the pellet pressure technique depends on the patient's condition. It should be light for children, pregnant women, and the elderly. This technique is particularly suitable for chronic and painful conditions, as it provides continuous stimulation, consolidates the therapeutic effect, and prevents relapse. Usually, both ears are alternately treated with pellet pressure.
Indications
(1) It has a good analgesic effect on various painful conditions.
(2) It has certain anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects on various inflammatory conditions.
(3) It has a beneficial regulatory effect on functional disorders, promoting the relief and recovery of symptoms.
(4) It has anti-inflammatory, desensitizing, and immune-improving effects on allergies and hypersensitivity reactions.
(5) It has an auxiliary therapeutic effect on endocrine and metabolic disorders, improving symptoms and reducing medication dosage.
(6) Others: It has effects such as promoting lactation and childbirth, preventing and treating transfusion and infusion reactions, as well as cosmetic, smoking cessation, drug addiction treatment, anti-aging, disease prevention, and health preservation.
Precautions
(1) Strict disinfection to prevent infection.
(2) For patients with sprains and movement disorders, appropriate movement of the affected area after needling can help improve the therapeutic effect.
(3) Pregnant women with habitual miscarriage should not receive acupuncture.
(4) Patients with severe organic diseases and severe anemia should not be needled. Strong stimulation should not be applied to patients with severe heart disease or hypertension.
(5) During ear acupuncture treatment, attention should also be paid to prevent syncope. If it occurs, timely intervention is necessary.
Expert Experience and Case Studies
The earlobe is an important part of the human body. When the organs, trunk and limbs, tissues, and organs of the body have diseases, various positive reactions appear at corresponding locations on the earlobe, such as decreased electrical resistance, decreased pain threshold, changes in color, deformation, desquamation, papules, and vascular congestion in related areas of the ear acupoint. The positive reaction points in the ear acupoint change at different stages of the occurrence, development, and outcome of the disease. Therefore, the ear acupoint can reflect the information of human diseases. It can not only reflect the location of the current disease, but also indicate past lesions. Some reactions may even indicate future diseases.
Typical Case: Thrombophlebitis
Tian, male, 42 years old. Redness, swelling, and pain on the inner side of the right lower leg for more than 3 months.
Medical History: No obvious cause. There is redness and swelling within a 20 cm range above the inner ankle of the right lower leg. The swelling is obvious and worsens after exercise. After treatment and taking Chinese herbal medicine, the redness and swelling have reduced. However, there is still a hard thread-like object at the superficial vein of the inner ankle, causing discomfort and affecting walking.
Physical Examination: There is a long thread-like object of about 10 cm along the great saphenous vein of the right lower leg. The local area is red and swollen, with pigmentation around it, and it is tender to touch.
Acupoints Selected: Corresponding areas, ear apex, sympathetic, endocrine, adrenal glands, heart, lungs, liver, subcortex, and Shenmen.
Treatment Effect: After 10 sessions of ear acupuncture (one course of treatment), the symptoms of thrombophlebitis have significantly improved.
| 1 2 > >> >>|