1. Definition of Cupping
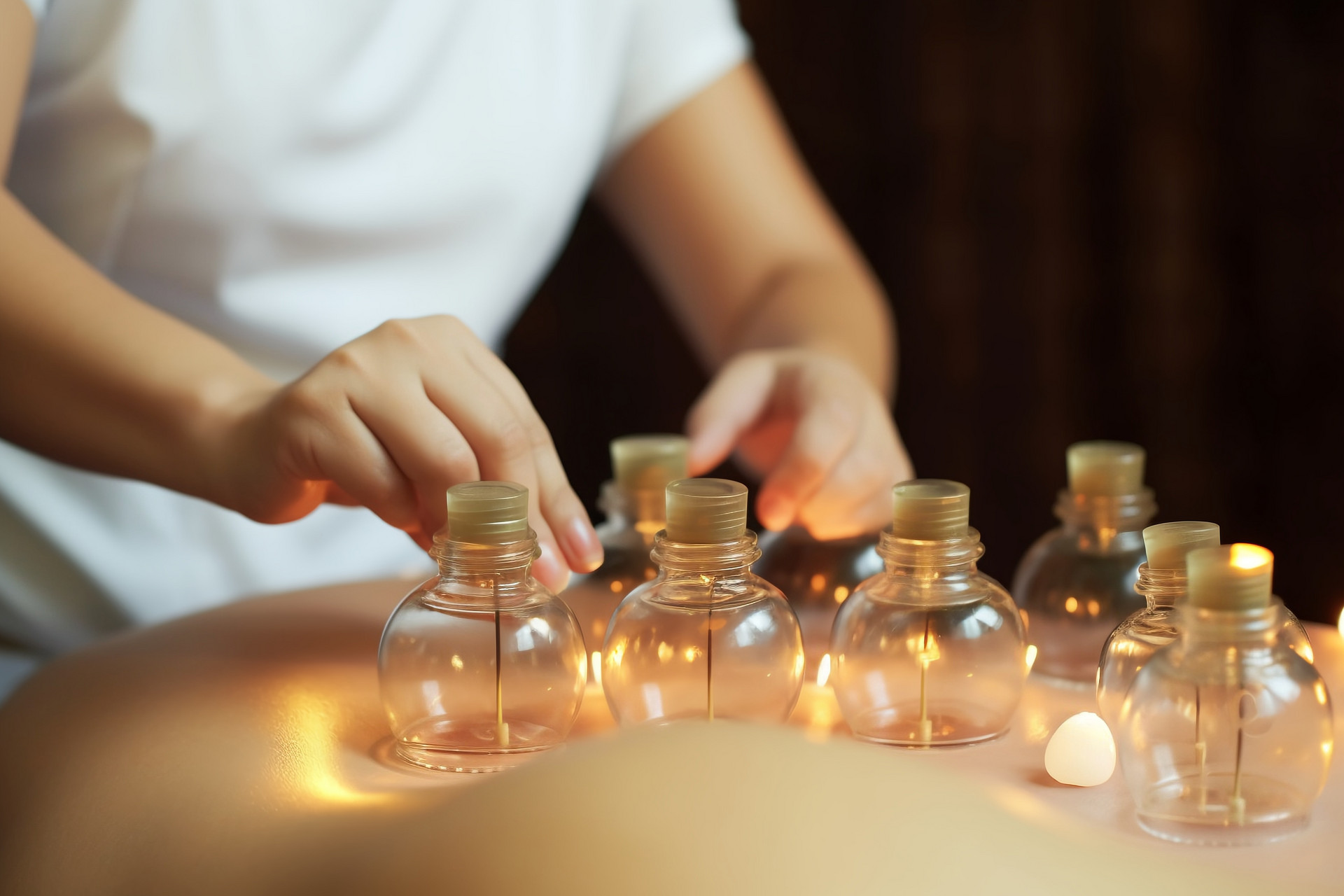
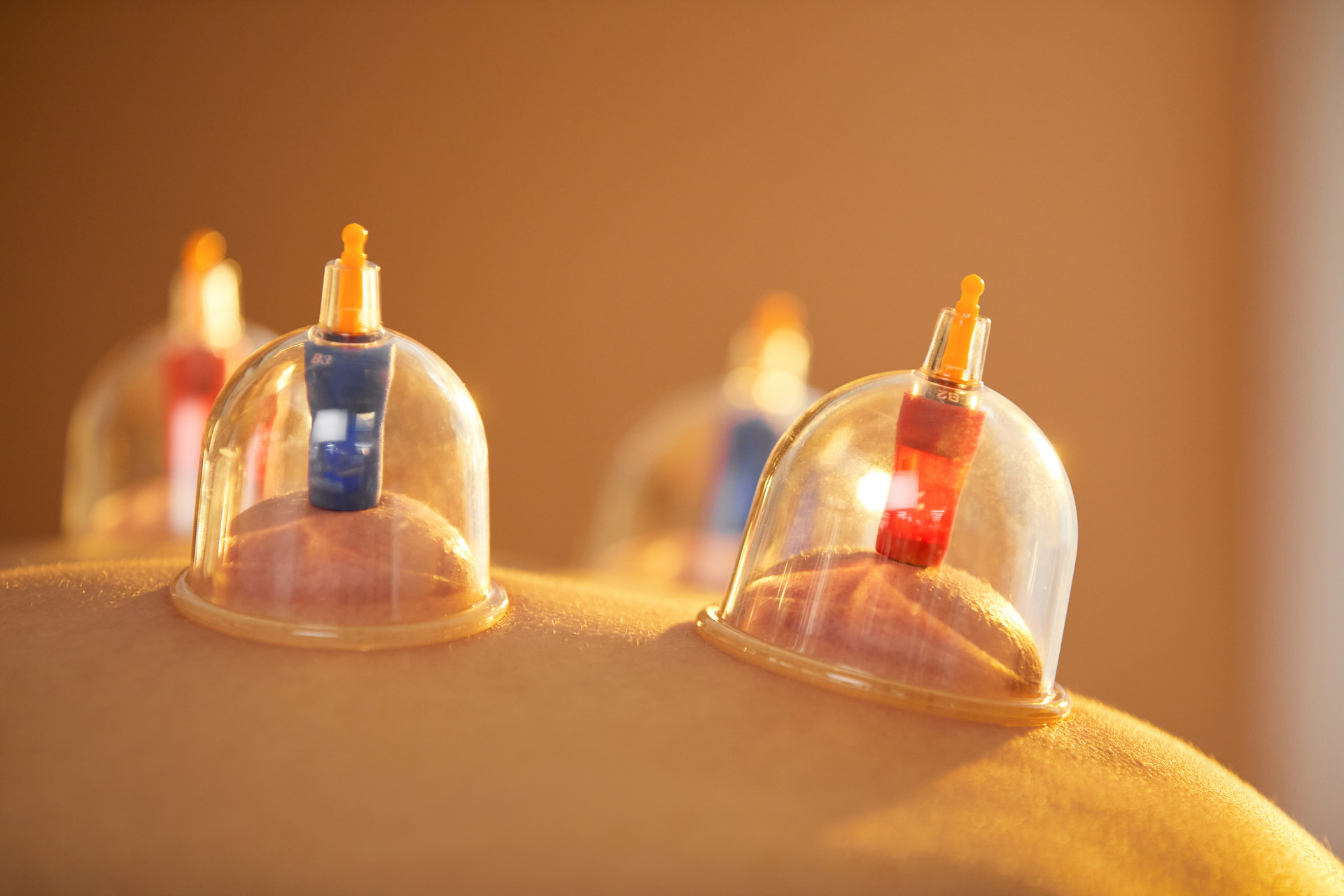
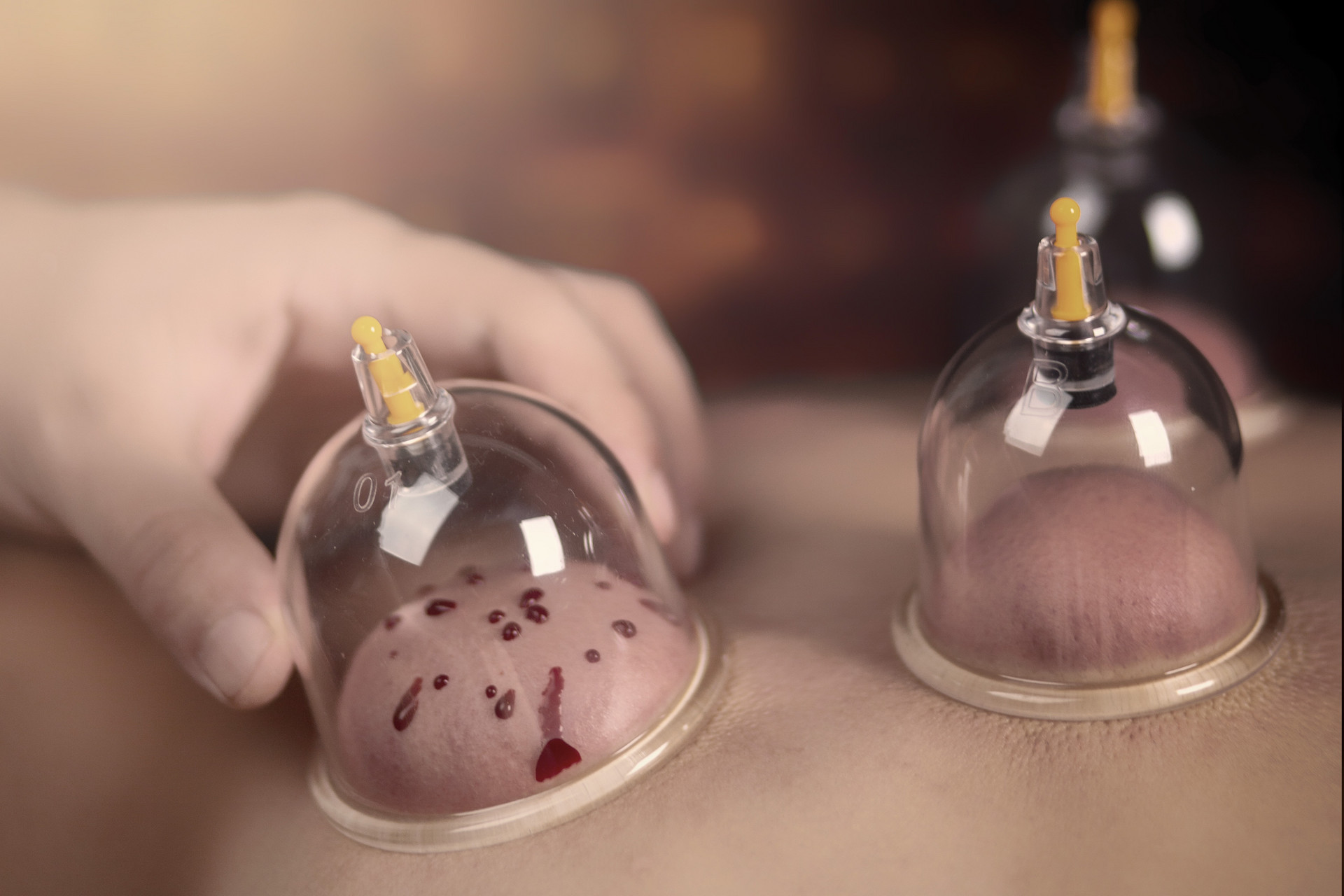
Cupping therapy is a method of external treatment that uses cups to create negative pressure by burning, heating, or suction, in order to remove the air inside the cups and apply them to acupuncture points or areas of the body that need treatment. This stimulates the body, causing congestion or blood stasis, and aims to regulate body functions, restore physiological balance, and eliminate diseases. It has the effects of warming the meridians, dispelling cold, promoting Qi circulation, activating blood circulation, relieving pain, reducing swelling, and detoxifying.
2. Historical Development of Cupping Technique
Cupping therapy has gradually evolved and developed through the long-term life and practice of the working people. It was formerly known as "horn therapy" because in ancient times people used the horns of animals (such as ox horns, sheep horns, etc.) to make hollow tubes, which were then used to puncture abscesses and suck out pus and blood. As early as the Warring States period, in the book "Fifty-Two Disease Formulas," there were already descriptions of the use of horn therapy for treating diseases: "For a male fistula located near the orifice, if it is large like a jujube, or small like a kernel, it should be sucked out with a small horn, which is about two dou of cooked rice in size, and the horn is stretched." The phrase "sucked out with a small horn" refers to the use of a small animal horn for extraction. In the Jin Dynasty, the famous physician Ge Hong also mentioned the use of cup-shaped instruments for cupping therapy in his book "Emergency Formulas Behind the Elbow."