1. Fuel
The fire can is a method of exhaust using heat. The commonly used fuels are ethanol cotton balls and paper strips. ① Ethanol cotton balls: Cotton balls dipped in a 75% to 95% ethanol solution are often used. If there is no ethanol available for cupping at home, high-proof white wine can also be used as a substitute. Ethanol, as a fuel, has high thermal energy and strong firepower. It can quickly remove the air in the cup, creating a large negative pressure and strong suction force. After covering the cup, the fire quickly goes out, reducing the risk of burning the skin. ② Paper strips: Paper strips are commonly used fuel for cupping. Thin and flammable paper should be selected, while thick, hard, and colored paper should be avoided. Thick paper has a low ignition point and insufficient heat, which affects the exhaust. If not careful, carbonization may occur, causing it to fall and burn the skin, so it is generally not suitable for use.
2. Disinfection and cleaning supplies
Ethanol degreased cotton balls are commonly used disinfection and cleaning supplies. They are used to clean the skin, disinfect the cups, and ignite the fire and exhaust during cupping.
3. Needles
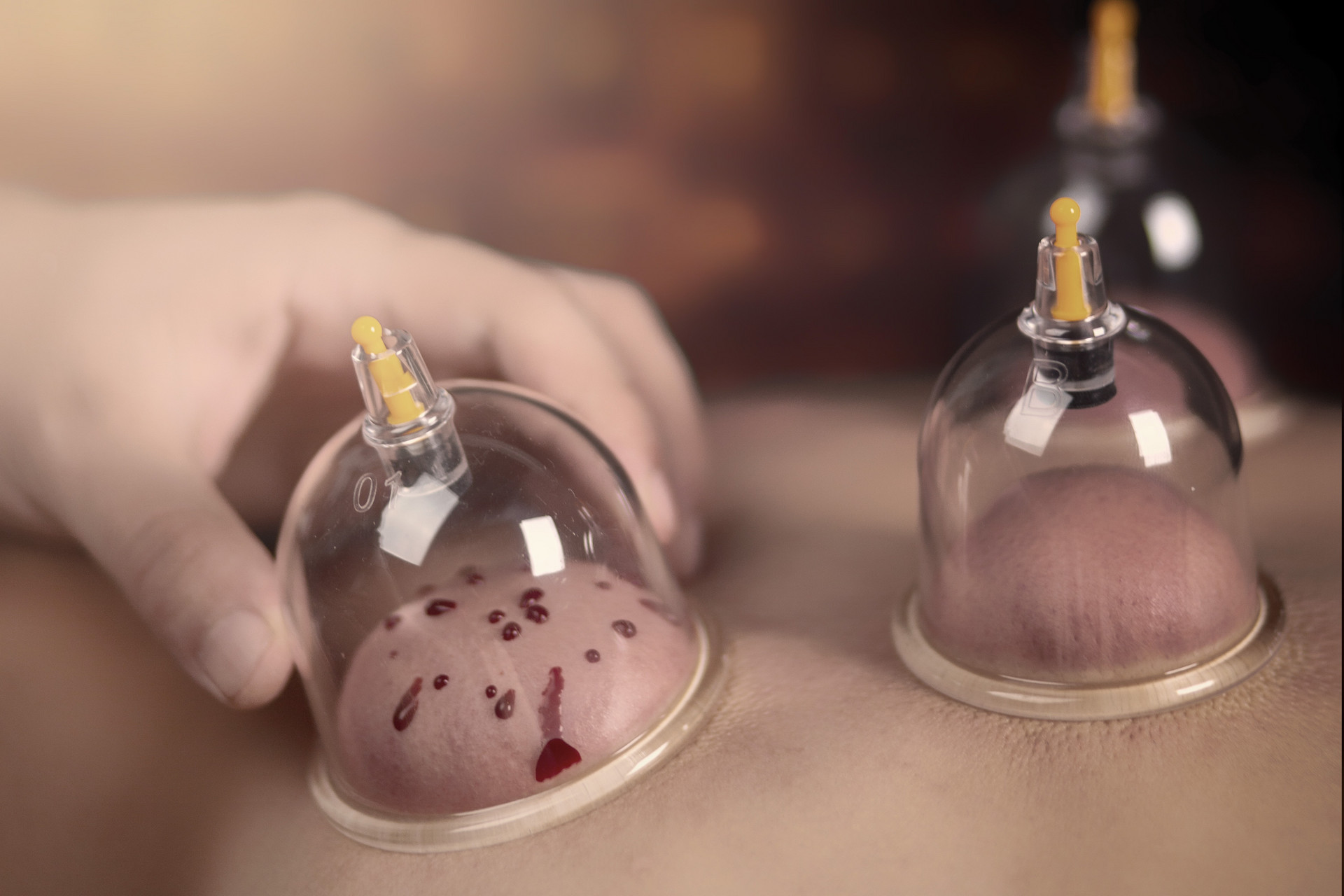
During cupping treatment, there may be a need for needle cups, bloodletting cups, etc. Therefore, it is necessary to prepare fine needles, triangular needles, and skin needles.
(1) Fine needles
Fine needles are one of the "Nine Needles" in ancient times, and they can be made of 18-gauge stainless steel wire with different lengths. For bloodletting therapy, fine needles of about 1 inch are generally suitable, especially for children and patients with weak constitution.
(2) Triangular needles
Triangular needles are made of stainless steel and are about 6 cm long. They consist of a needle body and a needle handle. The needle handle is cylindrical, and the needle body has three sides with blades on the tip. Triangular needles are available in large, medium, and small sizes. Thick fine needles, sewing needles, and injection needle heads can be used instead of triangular needles. They are suitable for adults and superficial venous bleeding, specifically for puncture and bloodletting.
(3) Plum blossom needles
Plum blossom needles, also known as skin needles or seven-star needles, have a history of one thousand years. The descriptions of "mao ci" and "yang ci" in the "Ling Shu Jing" have many similarities to the treatment with plum blossom needles. There are several types of plum blossom needles, with different names depending on the number of needles. Ancient people bundled 5 needles together, which looked like plum blossoms, so they were called plum blossom needles. When 7 needles were bundled together, they were called seven-star needles. When 18 needles were bundled, they were called arhat needles. In addition, because the needles are shallow and do not harm the flesh, they are also called skin needles.
There are two types of plum blossom needles: traditional needles and improved needles. The former is made by drilling a small hole at one end of a chopstick and threading 1 to 7 needles (usually using sewing needles) into the hole, leaving the needle shaft exposed, and then tying them with cotton thread to fix them. The latter has a screw cap at the front end of the needle, with a hole in the cap, and the needle is threaded through the hole and secured with the screw. The needle tip should not be too sharp and should be loose in shape. The needle handle should be firm and elastic, and the needle tips of the entire bundle should be even, to prevent skewing, hooking, rusting, and defects. In recent years, there have been cylindrical skin needles made of metal, called rolling needles. They have the advantages of a wide stimulation area, uniform stimulation, and convenient use. Plum blossom needles evolved from ancient steel needles. "Ling Shu Jiuzhen Shiyi Yuan" said, "Steel needles are large-headed and sharp-tailed, used to remove yang qi" and "mainly heat in the head and body." Plum blossom needles are suitable for superficial skin bleeding. Generally, they are pricked in the order of meridians, nerves, and muscle distribution, from top to bottom and from the outside to the inside, to achieve bloodletting.
4. Lubricant
Cupping therapy can be performed without lubricants, but for certain cupping methods, it is necessary to use a medium as a lubricant. The lubricant is generally applied to the treatment area and the mouth of the cup before the therapy to enhance the density between the skin and the cup and maintain the suction of the cupping device. Commonly used lubricants include Vaseline, liquid paraffin, and vegetable oil. Sometimes, for enhanced therapeutic effect, oil preparations with medicinal properties, such as red flower oil, turpentine oil, and massage lotion, are used to enhance blood circulation. The use of lubricants not only improves the treatment effect but also protects the skin from burns.
5. Medications
Depending on the patient's condition, some herbal decoctions can be selected and used after removing impurities. They can serve as lubricants and provide corresponding treatment for the patient's condition.