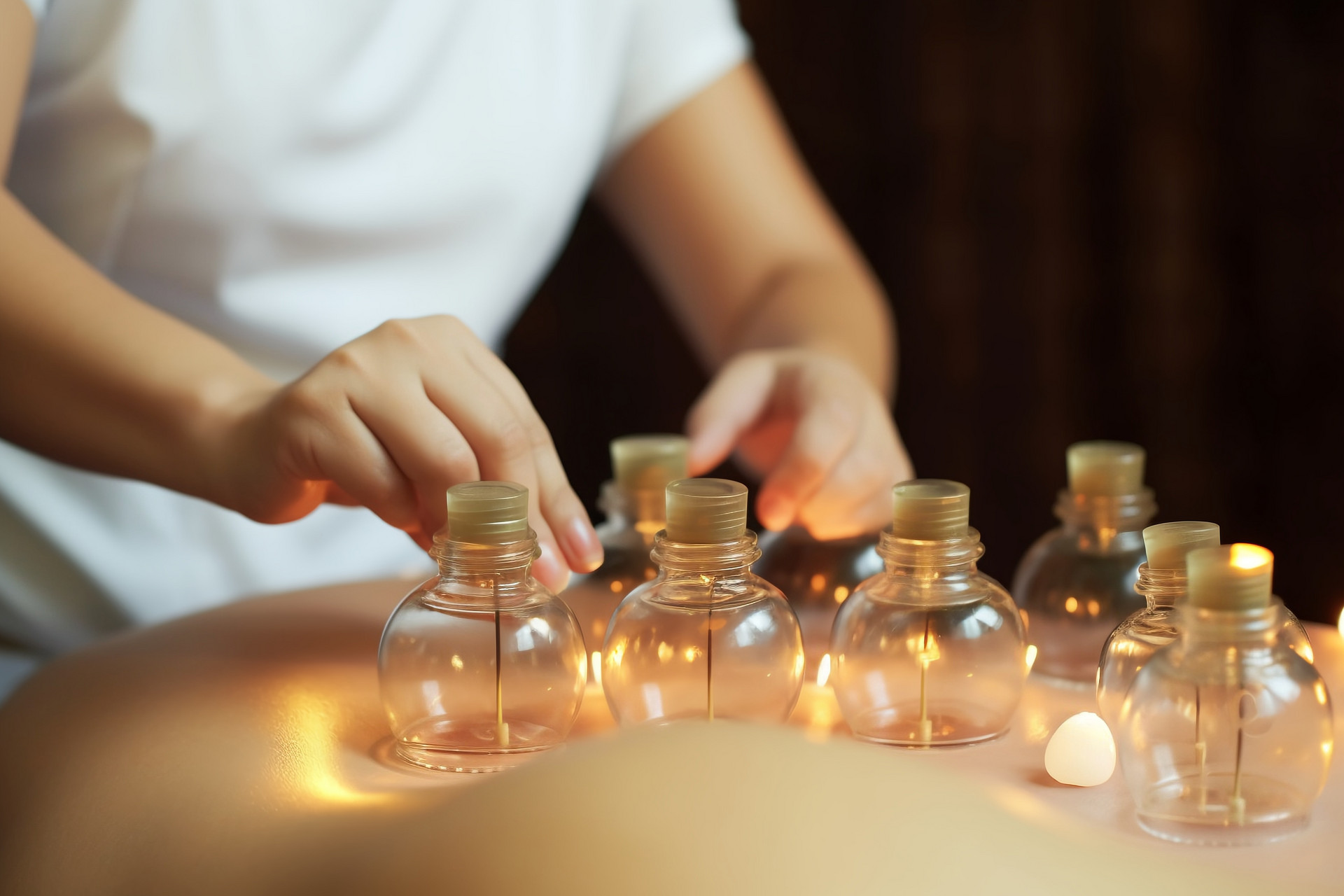
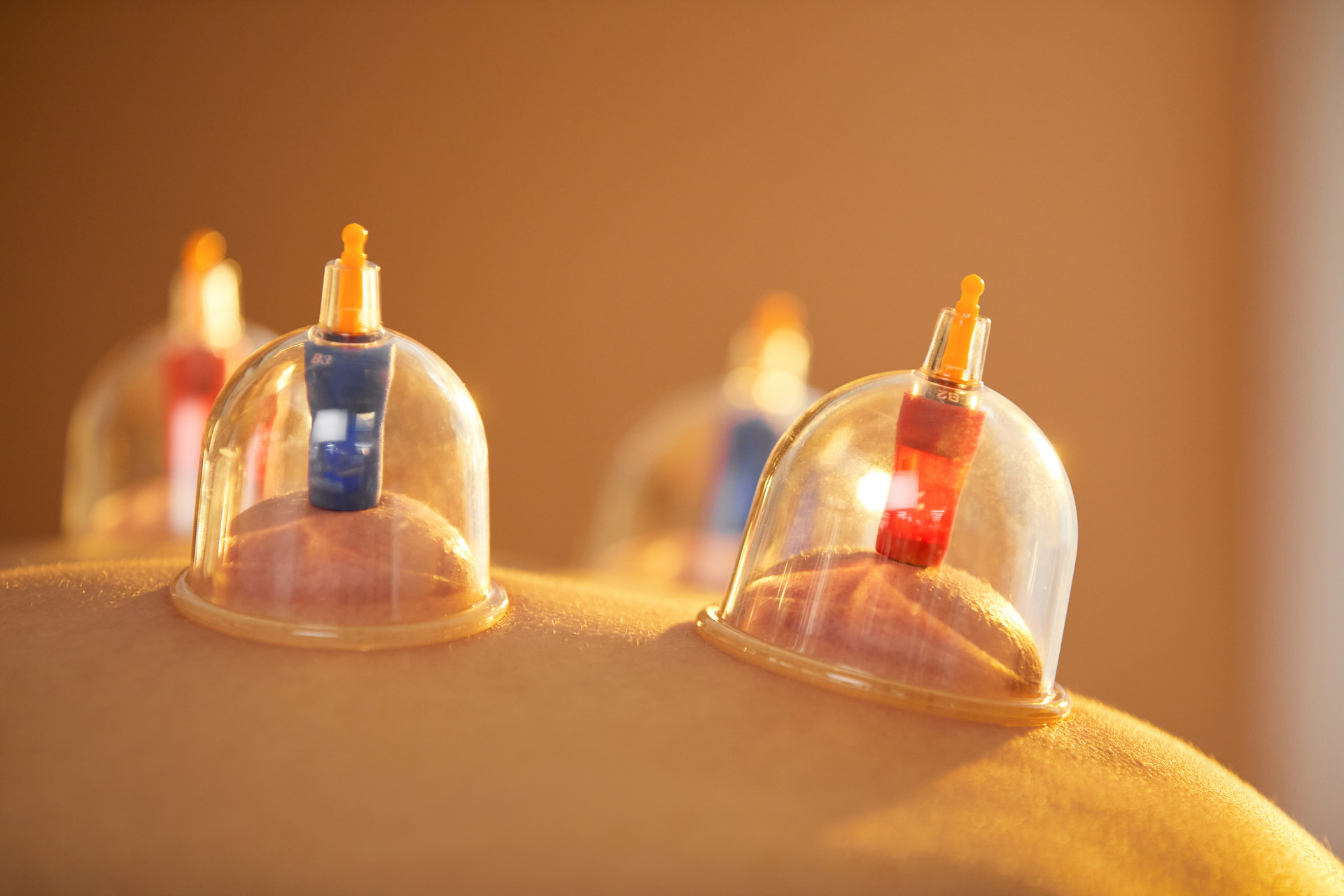
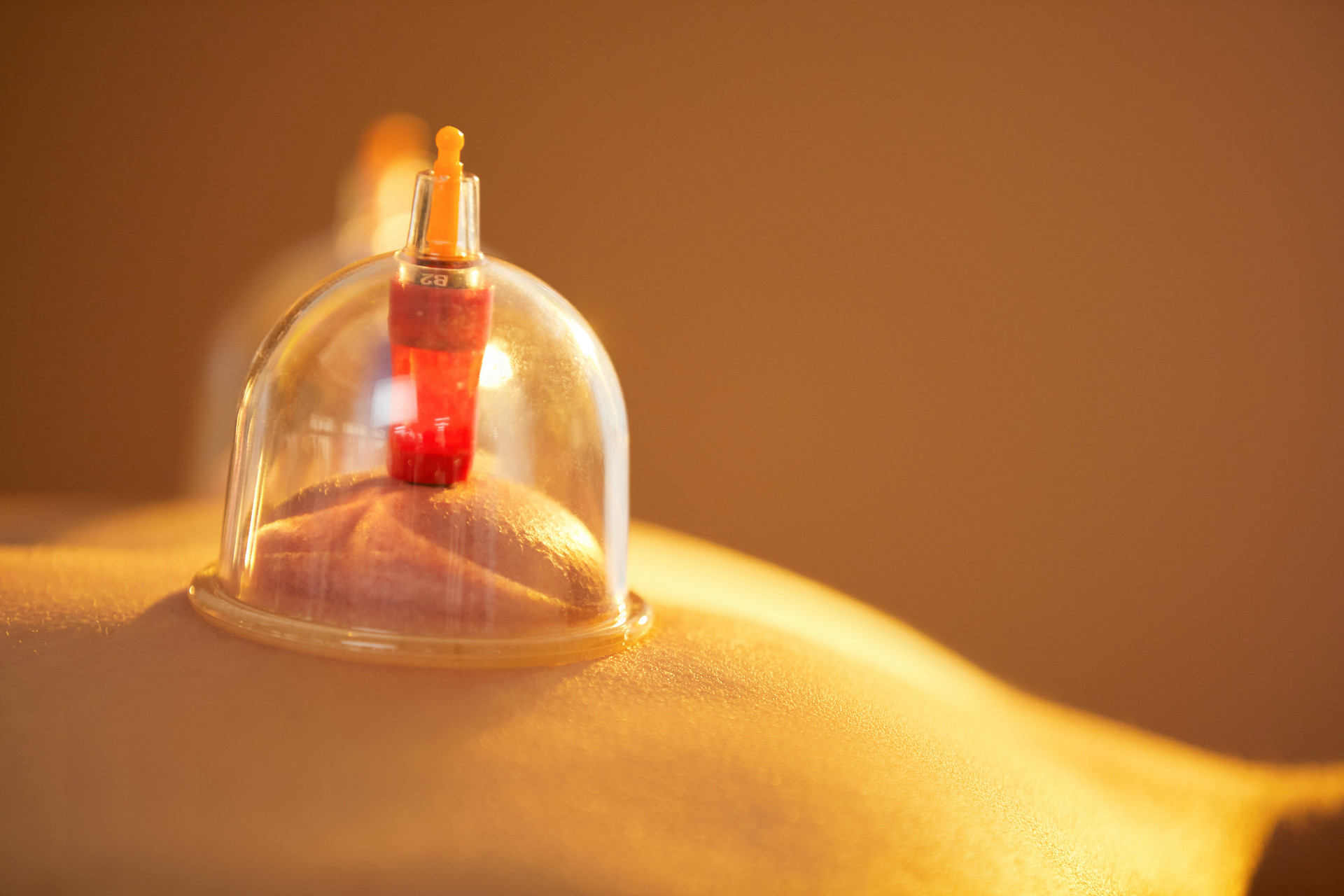
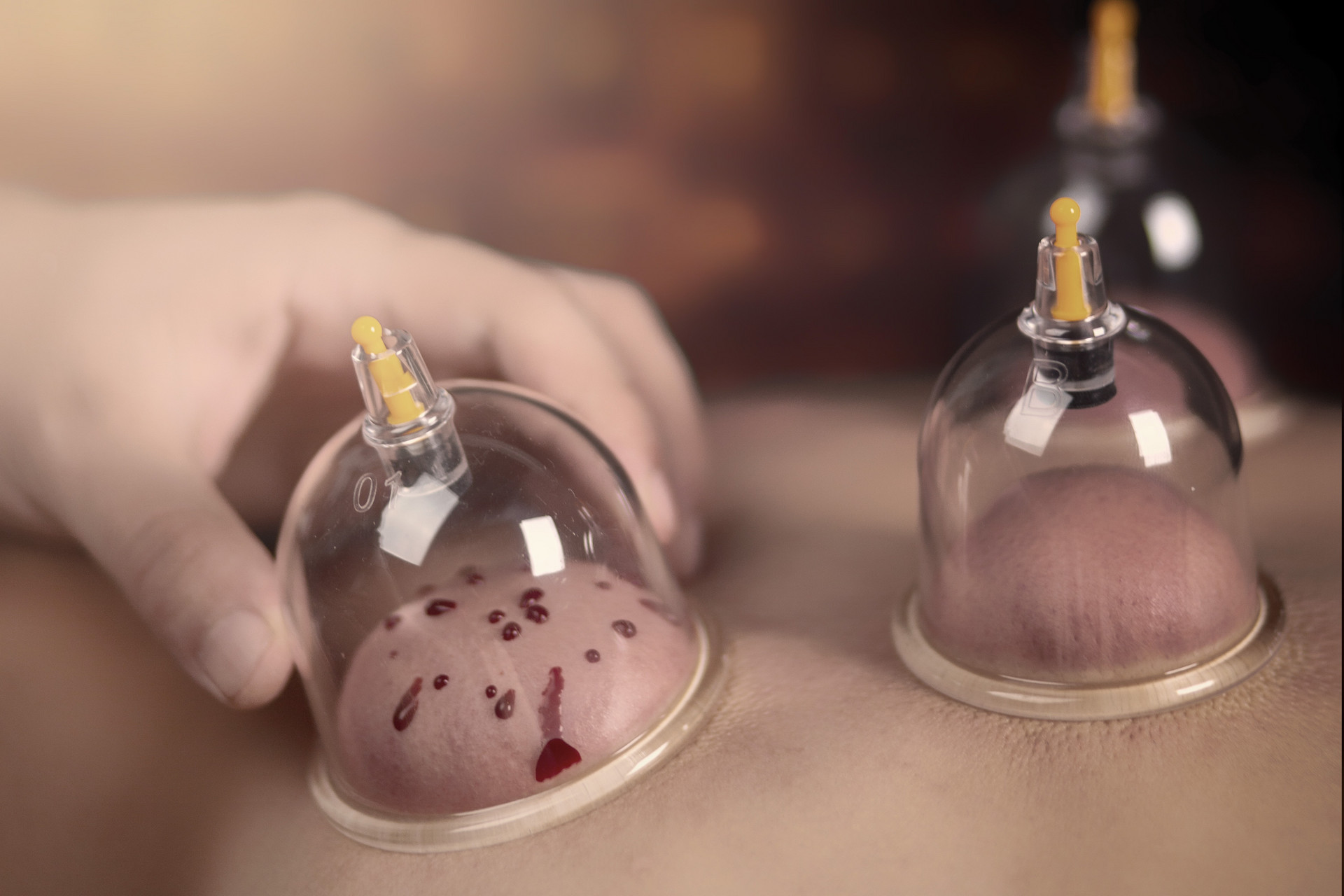
Cupping therapy is a treatment method that uses various cupping tools to create a negative pressure state on the body surface by burning or other methods, causing the cups to adhere to certain parts of the body, acupoints, meridians, or affected areas. By applying heat and negative pressure, it can increase the temperature and pressure of the treated area, accelerate blood circulation, and have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, blood circulation-promoting, blood stasis-removing, cold-expelling, and dampness-removing effects, achieving the biochemical effects of promoting meridian circulation and regulating qi and blood.
The control and mastery of cupping therapy time are of great importance and significance for treatment and therapeutic effects.
Below, I will briefly introduce my clinical experience and understanding to colleagues.
The control and mastery of cupping therapy time should mainly follow the guiding principles of "differentiating syndromes and differentiating diseases".
1. Differentiating syndromes
It mainly follows the principles of purging for excess syndromes - no cupping method, tonifying for deficient syndromes - cupping method with cups left on, and balancing tonifying and purging - flash cupping method.
No cupping method refers to immediately removing the fire cup from the body surface without further cupping treatment after it is attached.
Cupping method with cups left on refers to leaving the fire cup on the body for 3-5 minutes (short-duration cupping) or 5-10 minutes (long-duration cupping).
Flash cupping method, also known as flash-fire cupping, refers to quickly inserting the ignited stick into the cup, immediately removing it, attaching the fire cup to the treatment area, and then removing it again. Repeat this process until the local skin becomes reddened. Flash cupping method can be performed with a single cup for small-area operations, such as at the Shénquè acupoint, or with multiple cups for large-area operations, such as the waist, back, and lower limbs. When using a single cup for flash cupping, attention should be paid to the fact that the temperature of the cup increases after a period of use, and it should be replaced in time to avoid scalding the patient's skin.
2. Differentiating diseases
1. Distinguishing the severity and urgency of the disease
For mild diseases and chronic patients, the treatment time can be short; for severe diseases and acute patients, the treatment time should be longer.
For patients with mild diseases and acute courses, the treatment time is relatively longer, while for patients with severe diseases and chronic courses, the interval between treatments is relatively shorter.
2. Distinguishing the affected area
For the face, cupping is generally not recommended. This is because the face has abundant capillaries, which can easily leave bruises and affect aesthetics, or even cause burns and disfigurement.
For the chest, it is better not to leave the cups on.
For the abdomen, flash cupping method is recommended.
For the neck, shoulders, and upper limbs, cupping method with cups left on can be used as needed.
For the waist, back, buttocks, and lower limbs, cupping method with cups left on is recommended.
3. Distinguishing the specific physical condition of the patient
For elderly patients with poor physical condition, the treatment time should be short, and the interval between treatments should be long. For young patients with good physical condition, the treatment time can be slightly longer, and the interval between treatments can be shorter.
Cupping therapy is not suitable for certain special populations. Patients with poor blood coagulation mechanisms, pregnant women, certain severe or infectious diseases, patients with skin diseases, and patients who are intoxicated, excessively hungry or full, or emotionally unstable should not undergo cupping therapy.