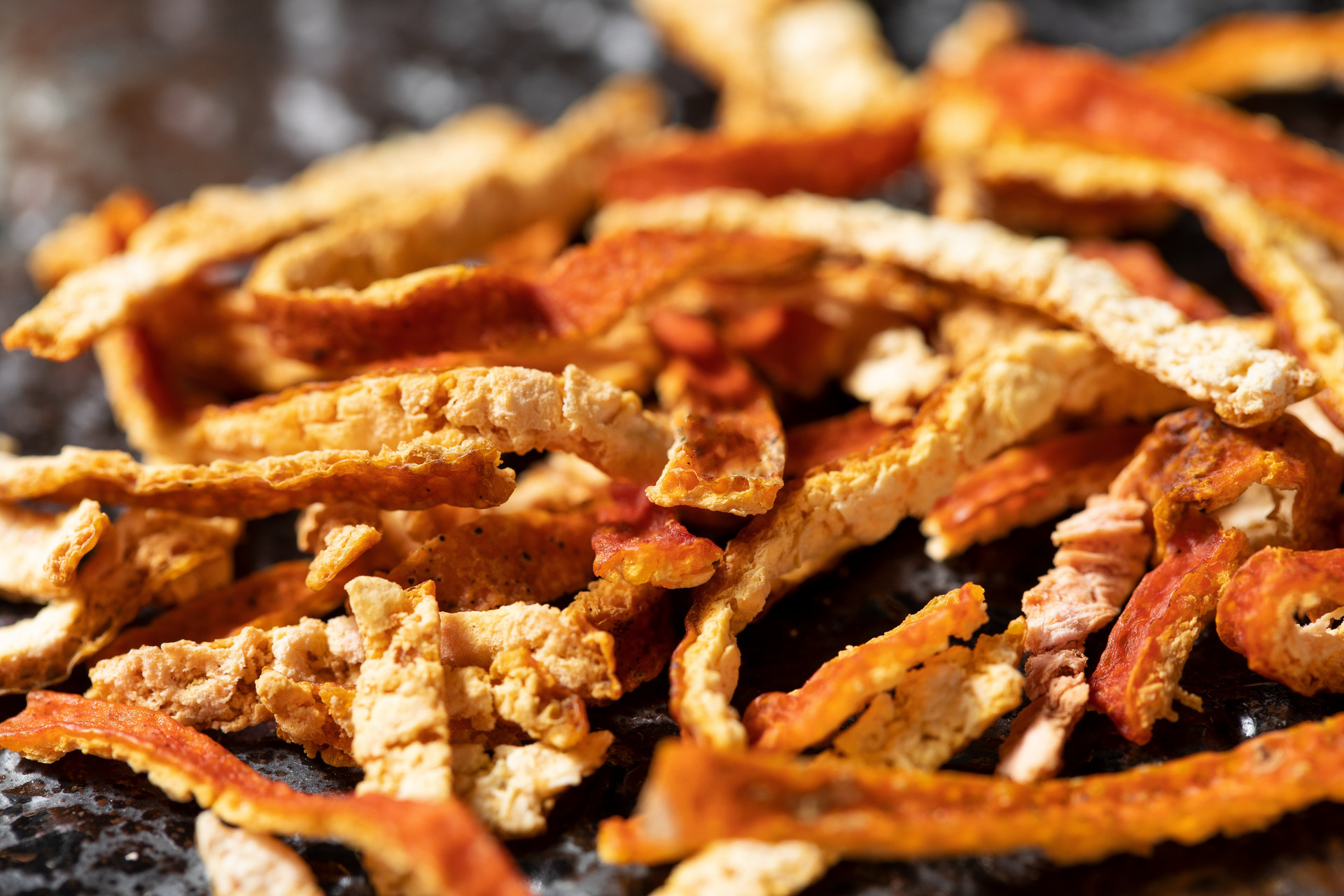
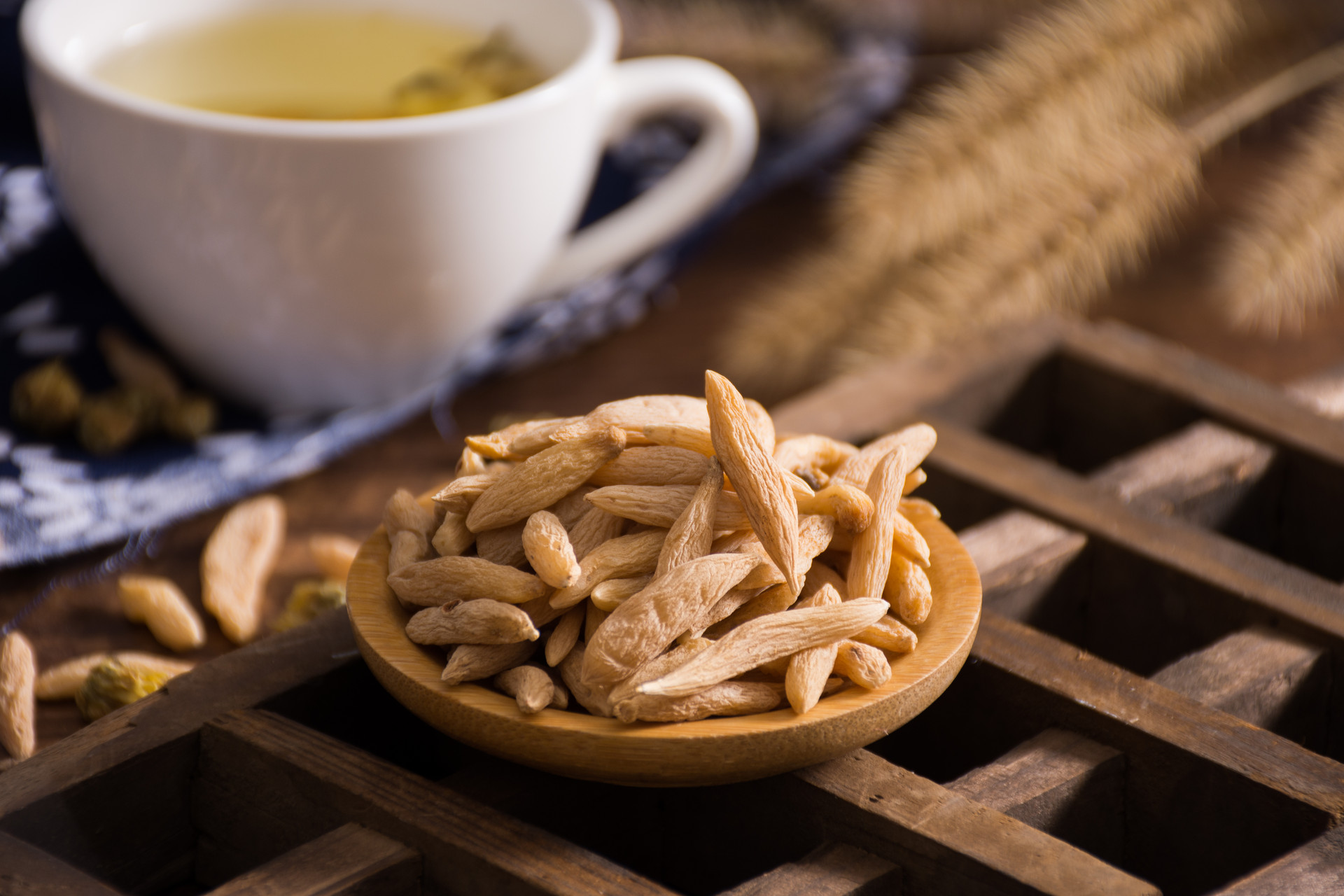
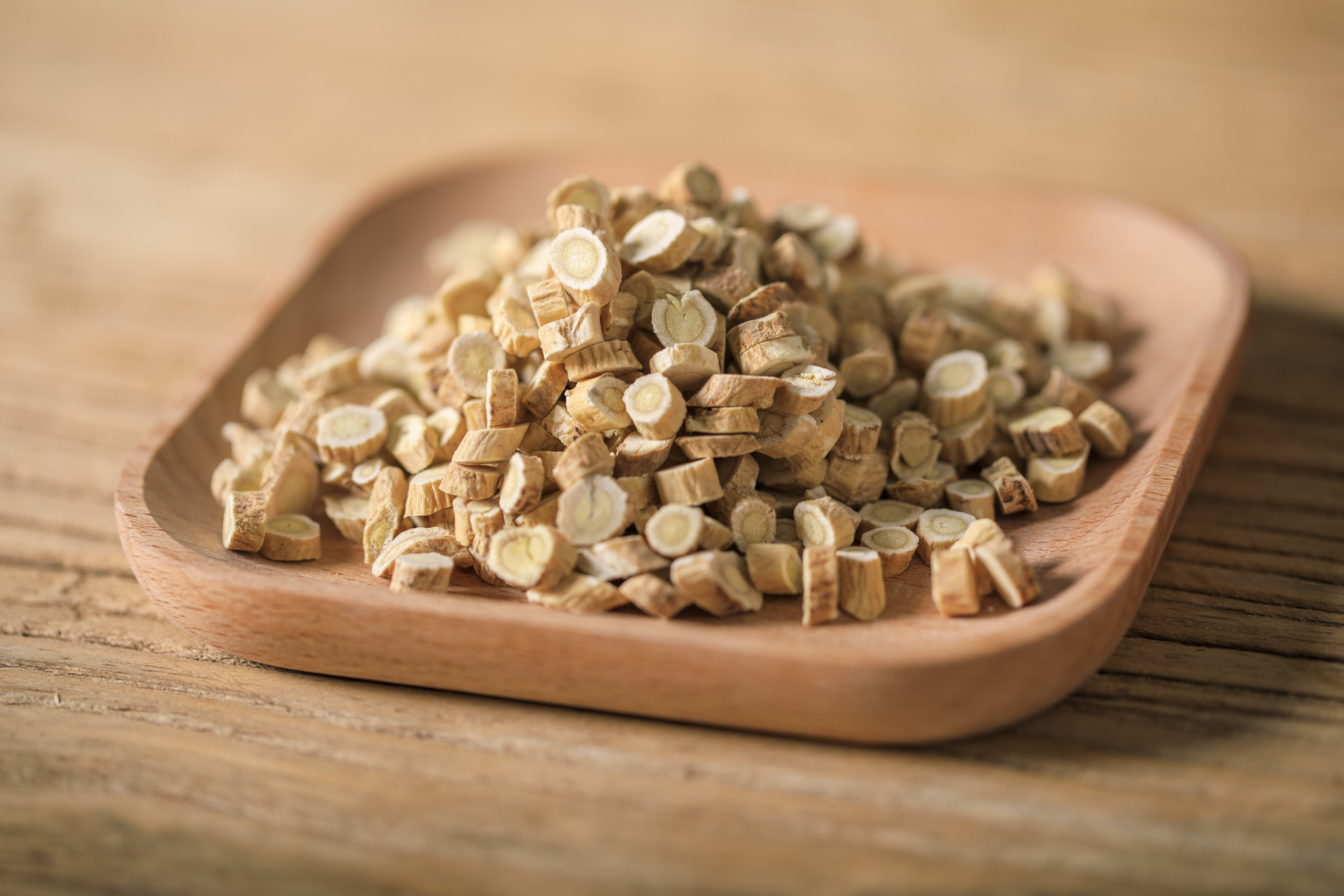
Shenjiang, also known as Gusuibu, Monkey Ginger, or Maojiang, is the rhizome of the plant family Osmundaceae, such as Osmunda japonica. It is warm in nature and bitter in taste, and enters the liver and kidney meridians. Shenjiang has the effects of nourishing the kidney and strengthening bones, promoting wound healing, and relieving pain. It is used to treat symptoms such as kidney deficiency and lower back pain, chronic diarrhea due to kidney deficiency, tinnitus and hearing loss, loose teeth, bruises, fractures, and other injuries. It can also be applied externally to treat bruises, alopecia areata, vitiligo, and other conditions. The "Annotations on the Classic of Materia Medica" states: "Shenjiang is used to control bleeding, stop bleeding, and promote wound healing. It can prevent stasis of blood and prevent excessive blood flow. It can also treat injuries as if they have not been injured before." Modern pharmacological studies have shown that the decoction of Shenjiang can stimulate compensatory proliferation of articular cartilage cells, promote bone healing, and reduce the incidence of bone and joint diseases. Its content of dihydroflavonoid glycosides can increase the beating frequency of cardiac cells, make contractions more powerful, and have a pacemaker effect on myocardial cells. It can significantly prevent the increase of serum cholesterol and triglycerides and prevent the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the aortic wall.
In clinical practice, Shenjiang is often used in combination with other herbs such as Duzhong, Fuzi, and Shan Zhu Yu to warm the kidney, strengthen the lower back, and strengthen the bones. It can be combined with natural copper, roasted turtle shell, and myrrh to treat tendon and bone injuries that are accompanied by persistent pain. For kidney deficiency with symptoms of deafness and tinnitus, it can be used together with Shu Di Huang, Shan Zhu Yu, Fu Ling, Mu Dan Pi, and Ze Xie. When used externally for bruises, sprains, fractures, and swelling and pain, it can be mashed with an equal amount of fresh ginger and applied to the affected area. For joint dislocation and fractures, it can be mashed with Cortex Eucommiae and an appropriate amount of flour to form a paste, which can be applied to the injured area. It is important to note that it should be used with caution in cases of yin deficiency with internal heat and without blood stasis.