Poria cocos, also known as pig's hoof fungus or wild boar food, is the dried sclerotium of the plant Poria cocos. It can be harvested throughout the year in the southern regions, while in the northern regions, it is mostly harvested in summer and autumn. Poria cocos has a neutral nature and a sweet and bland taste. It enters the spleen, kidney, and bladder meridians. It contains components such as ergosterol, biotin, carbohydrates, and proteins. It has the effect of diuresis and dampness elimination. It is used to treat symptoms such as difficult urination, edema, athlete's foot, diarrhea, cloudy urine, and abnormal vaginal discharge. It is considered as a medicine that "eliminates dampness, promotes water passage, and balances yin and yang" (Compendium of Materia Medica). However, there are counterfeit products in the market, where the sclerotium of another plant is disguised as Poria cocos. Care should be taken to distinguish them when using.
Authentic Poria cocos:
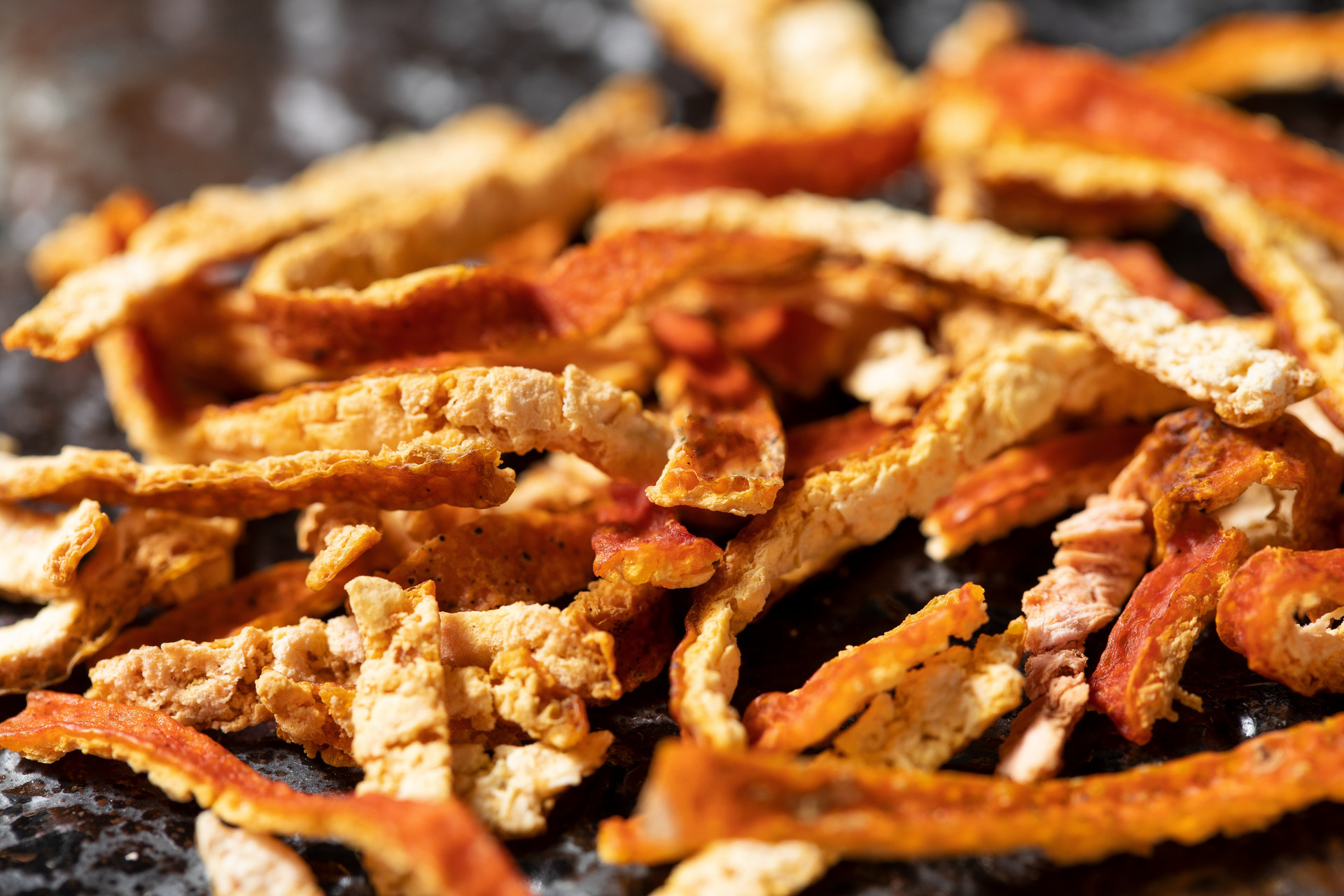
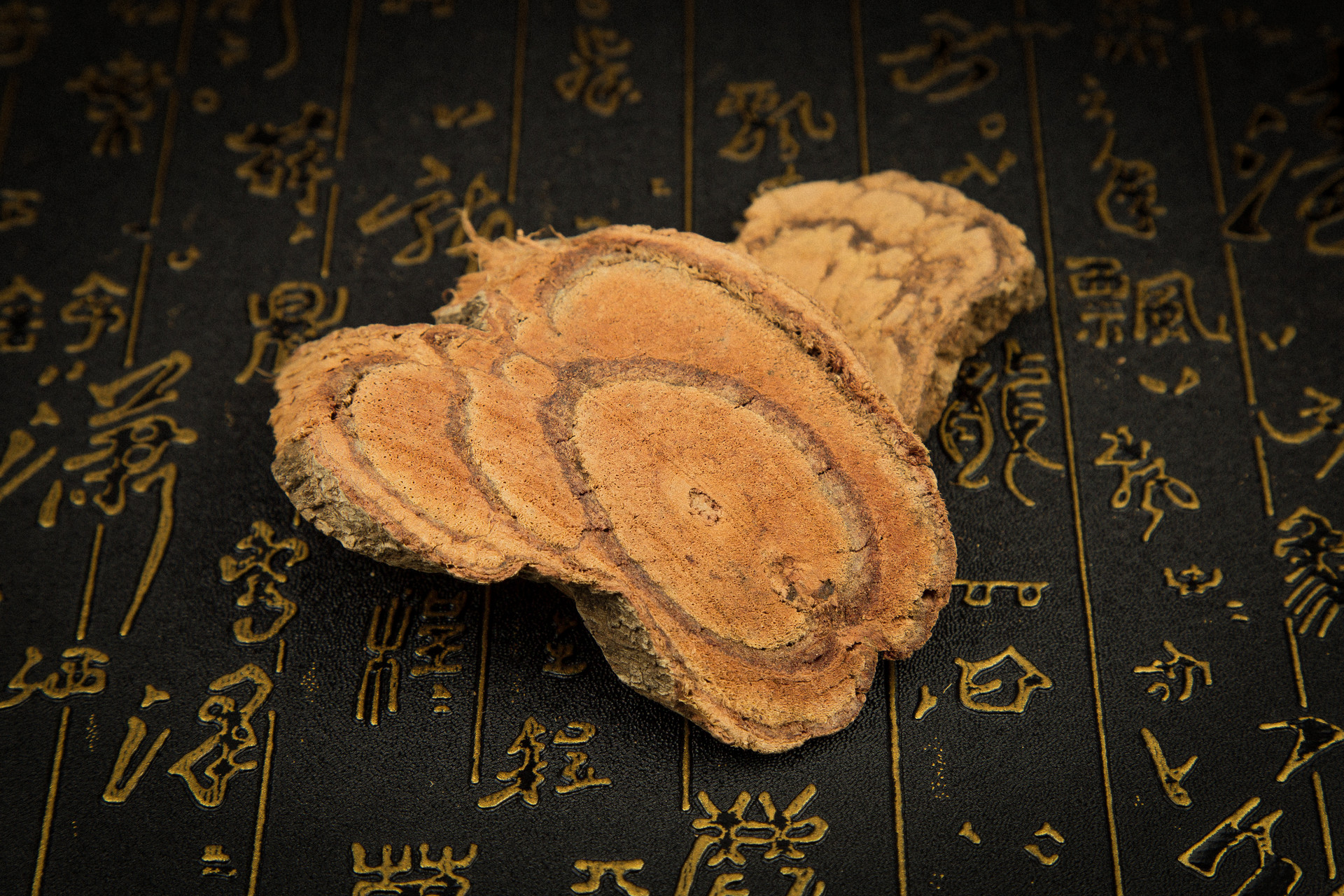
The authentic Poria cocos is dried and irregularly shaped, either long and curved or branching. It resembles ginger, with a length of about 10-25 cm and a diameter of about 3-8 cm for the long-shaped ones, and a diameter of about 3-7 cm for the round-shaped ones. The surface is gray-black or brown-black, with protuberances and obvious wrinkles. The texture is firm but not solid, light like cork, and the cross-section is fine and white or light brown, slightly granular. When sliced and placed in water, it absorbs water slowly. It has no odor and tastes bland.
Counterfeit Poria cocos:
The counterfeit Poria cocos is very similar in appearance to the authentic one, but the surface is gray-white and smooth, without protuberances and wrinkles. The texture is chewier and more difficult to break, but it tears easily. The cross-section is uneven, and when sliced and placed in water, it quickly absorbs water and expands. It also has a weak odor and tastes bland.
Modern pharmacological research has confirmed that Poria cocos decoction does have a diuretic effect, but its potassium content is not high, nor does it dilute the blood. Its diuretic effect may be due to the inhibition of repeated absorption of electrolytes and water in the renal tubules. Its alcohol extract has inhibitory effects on Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. In recent years, studies have also found that Poria cocos extract has inhibitory effects on various tumors, such as lung cancer, liver cancer, bladder cancer, esophageal cancer, leukemia, and nasopharyngeal cancer. Counterfeit Poria cocos does not possess the aforementioned effects and cannot be used as a substitute for authentic Poria cocos in medicine. Careful identification should be done to avoid misusing and delaying treatment.