Ginseng, also known as: mountain ginseng, club hammer, round ginseng, is the dried root of the ginseng plant, a member of the Araliaceae family. The flowers and leaves of ginseng can also be used medicinally. The ginseng that people commonly refer to is the root of ginseng. Ginseng has the effects of "tonifying qi, consolidating sweating and generating fluid, and calming the mind. It is used to treat symptoms such as exhaustion, poor appetite, fatigue, nausea and vomiting, loose stools, asthmatic cough, spontaneous sweating, palpitations, forgetfulness, dizziness, headache, impotence, frequent urination, thirst, excessive menstrual bleeding in women, slow convulsions in children, and chronic deficiency of qi, blood, and body fluids." It is a precious and valuable medicinal herb.
The following are common counterfeit ginseng products:
1. The root or lateral root of the burdock plant in the Asteraceae family.
2. The root of the Dipsacaceae plant Dipsacus asper.
3. The root of the Allium chinense, a plant in the Asteraceae family.
4. Garden ginseng soaked in water and then sold as mountain ginseng.
The identification points and methods for the above counterfeit ginseng:
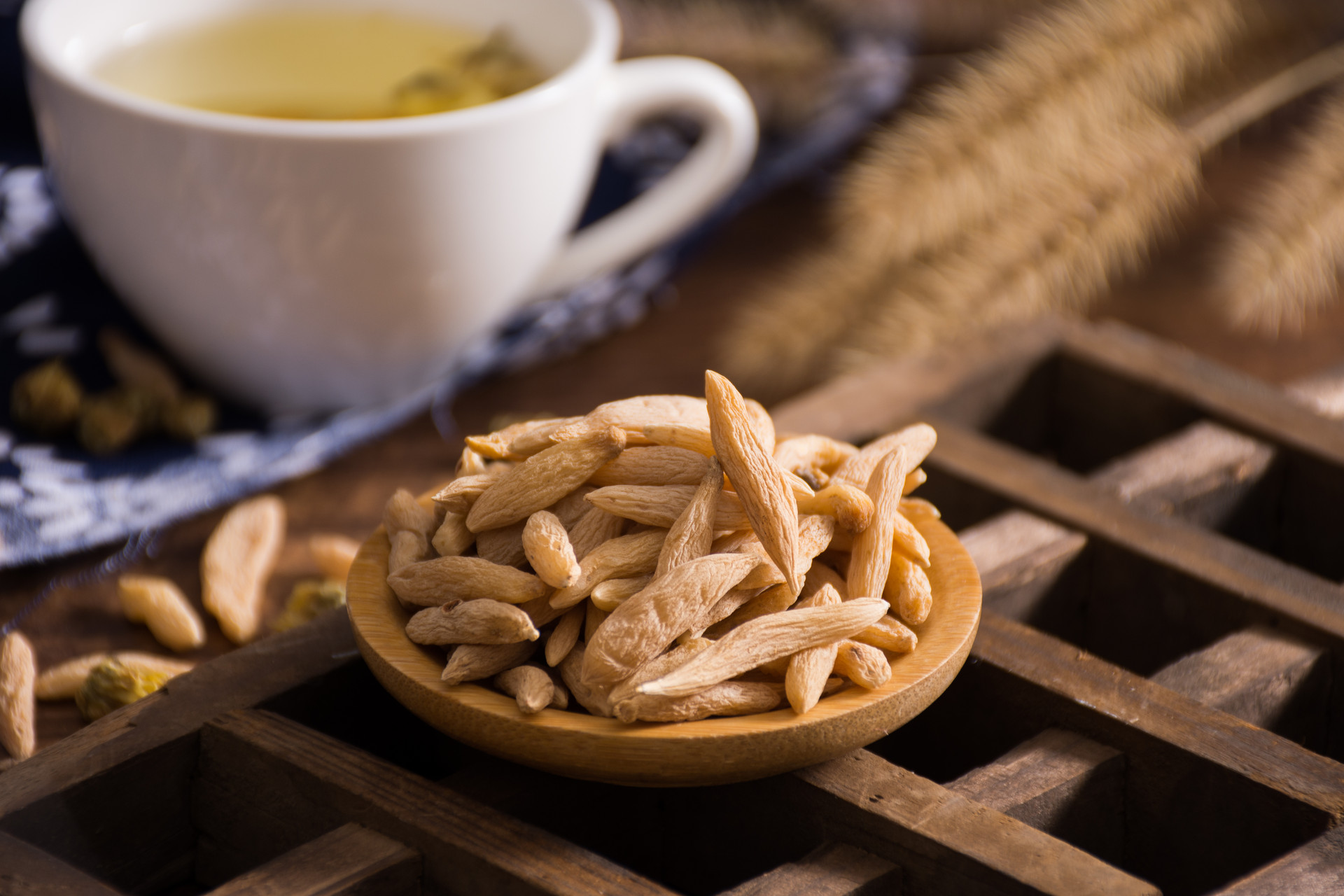
Wild ginseng (mountain ginseng) has a main root that is the same length as or shorter than the rhizome, with a length of 3-10 centimeters. It has a triangular, cylindrical, or rhomboid shape. The surface is grayish-yellow with longitudinal striations, and the upper end of the ginseng has tightly spaced and deeply recessed annular striations. The root hairs are long and thin, clear and orderly, and the lower part has multiple branches, with prominent wart-like protrusions, commonly known as "pearl nodules." The thin, long rhizome has dense stem marks, and the adventitious roots are relatively large and resemble jujube pits.
Cultivated ginseng (garden ginseng) has a main root that is cylindrical or spindle-shaped, with a diameter of 1-2 centimeters and a length of 3-15 centimeters. The surface is yellowish in color, and longitudinal wrinkles and shallow, intermittent coarse transverse wrinkles can be seen on the upper part or the entire root. There are 2-3 lateral roots at the lower part, with numerous thin and long root hairs, and occasionally inconspicuous small wart-like protrusions growing on the root hairs. The rhizome (bud head) has a diameter of 0.3-1.5 centimeters and a length of 1-4 centimeters. It is often twisted and curved, with adventitious roots and sparse stem marks in the form of depressions. The bark has brownish-yellow resin canals and radial cracks. The texture is hard, and when cut, the cross-section is pale yellowish-white, powdery, and the annular rings of the cambium are brownish-yellow. It has a distinctive aroma and a slightly bitter and sweet taste.
The morphology of burdock root is elongated, cylindrical, or spindle-shaped. The surface is brownish in color, and the root branches are few. It has obvious longitudinal wrinkles and grooves, with yellowish-brown bark. The texture is tough, and when cut, the cross-section appears translucent and gelatinous. The annular rings of the cambium are relatively clear, and the wood is yellowish-white with radial texture. It has a slight aroma and a slightly bitter and astringent taste.
The morphology of Dipsacus asper root is elongated and cylindrical, with branches or no branches. The length is 30-40 centimeters. The head near the root has annular striations, and the middle and lower parts have obvious longitudinal wrinkles and grooves, with a twisted shape. The texture is tough and horny. After cutting, the bark is narrow, brownish, and the annular rings of the cambium are brownish in color. The wood is wide, yellowish-white, with radial texture. It has a slight aroma and a sweet taste.
The morphology of garden ginseng soaked in water is relatively straight and elongated, with a grayish-yellow surface. It is about the same length as the rhizome, about 4 centimeters. The upper end can be seen with more intermittent annular striations, and the lower end can be seen with obvious longitudinal wrinkles. The root hairs are few, short, and brittle, with 3 lateral roots. The wart-like protrusions on the lateral roots are not obvious. The rhizome has sparse nodes in the shape of a ladle, arranged alternately, and has 3 longitudinal bodies. Upon closer inspection, it can be seen that the main root, rhizome, lateral roots, and root hairs are all made by bonding. They will disintegrate when soaked in water.