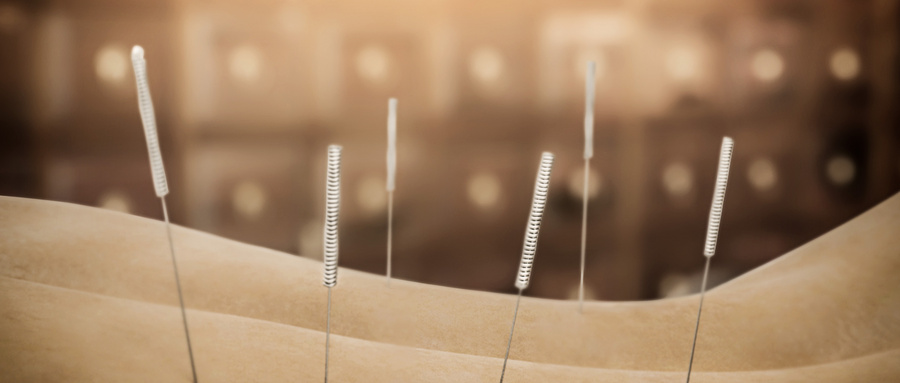
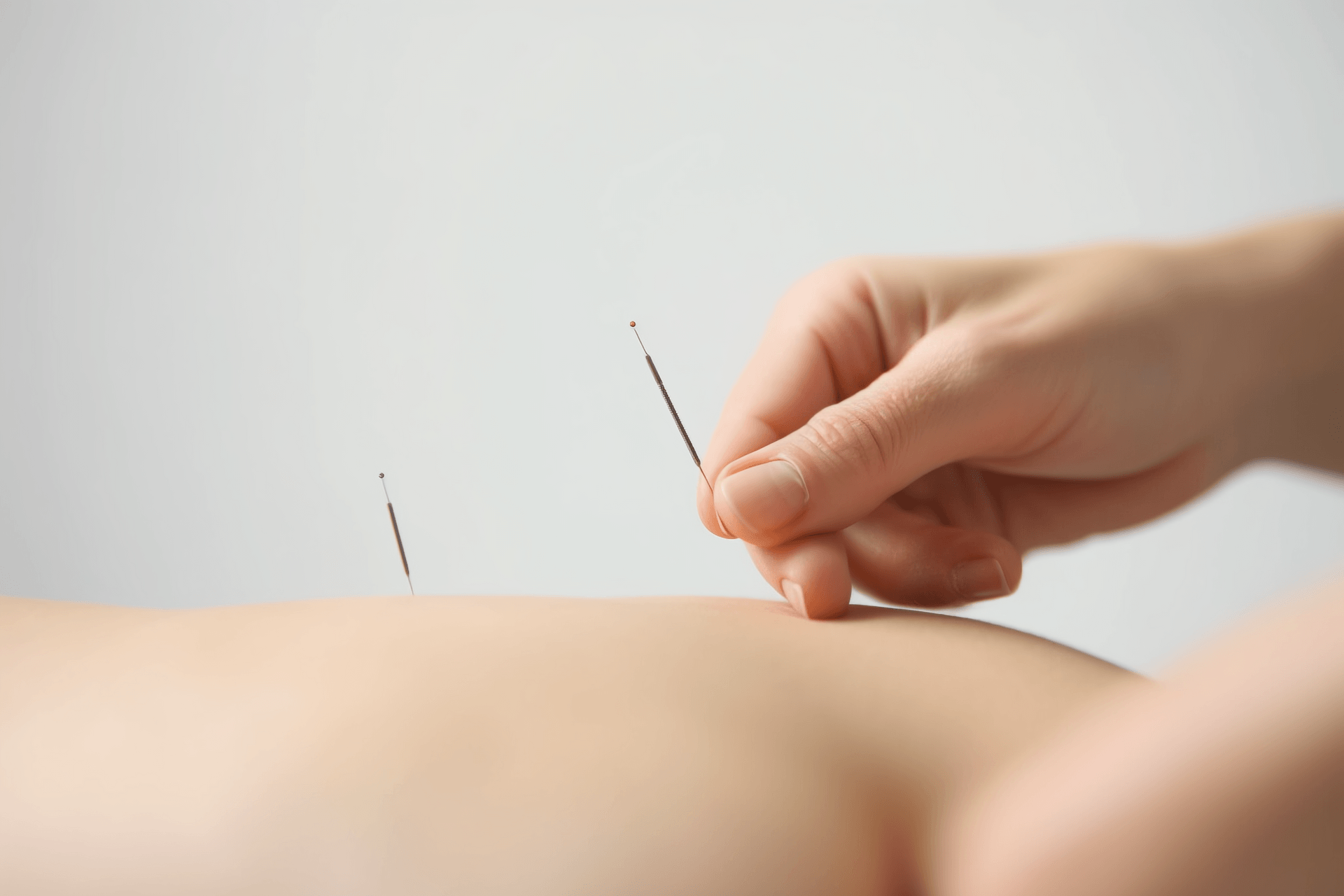
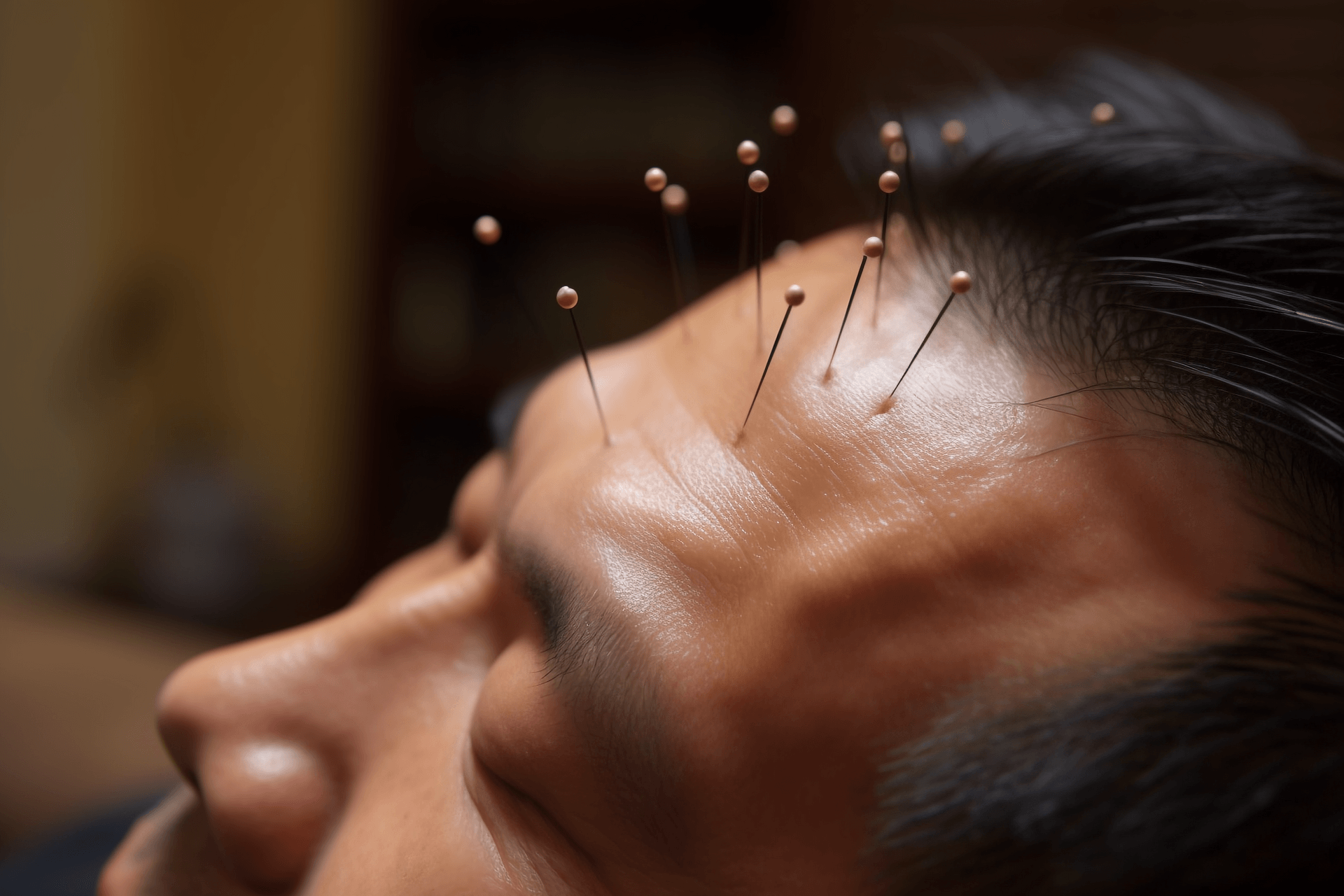
Just like taking medicine, acupuncture also requires mastery of "dosage". However, for a long time, acupuncture treatment has lacked standardization. Not only do doctors and practitioners have different techniques, but also the assessment of treatment efficacy mainly relies on the "clinical feeling" of both the doctor and the patient. The research team led by Academician Shi Xuemin from the First Affiliated Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine is currently conducting a research project titled "Quantitative and Biological Basis of Acupuncture Techniques" funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology as a major theoretical research project in 2009. This project aims to quantify acupuncture treatment techniques and clarify the "four elements of acupuncture technique": needle insertion direction, depth, technique duration, and the duration of the effective therapeutic effect of a single operation. It aims to standardize, regulate, and modernize the field of acupuncture.
As early as 1973, Academician Shi Xuemin proposed the concept of "quantitative study of acupuncture techniques". Through in-depth study of ancient medical books and summarizing clinical experience, Academician Shi Xuemin quantified and standardized acupuncture techniques based on the frequency, amplitude, and direction of twisting the needle. Through various basic experimental studies such as hemodynamics, he ultimately determined and scientifically defined the four elements of acupuncture technique: needle insertion direction, depth, technique duration, and the duration of the effective therapeutic effect of a single operation. Based on the theory of the "four elements of acupuncture technique", the research team from the First Affiliated Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine selected mature treatment models that have been proven effective in clinical practice, including acupuncture at the Jianying point for the treatment of primary hypertension, acupuncture at the Renzhong point for the treatment of ischemic stroke, and acupuncture at the Fengchi point for the treatment of insufficient blood supply in the vertebrobasilar system. They have explored the role of the "four elements of acupuncture technique" in acupuncture effects and initially clarified the quantitative relationship between acupuncture technique and treatment efficacy. Currently, the research is being conducted through metabolomics, genomics, proteomics, neuroendocrinology, and other approaches, and has achieved significant results. Ultimately, it is expected to systematically reveal the effects of meridians and the quantitative relationship between acupuncture techniques and treatment efficacy, thereby improving the clinical effectiveness of acupuncture.