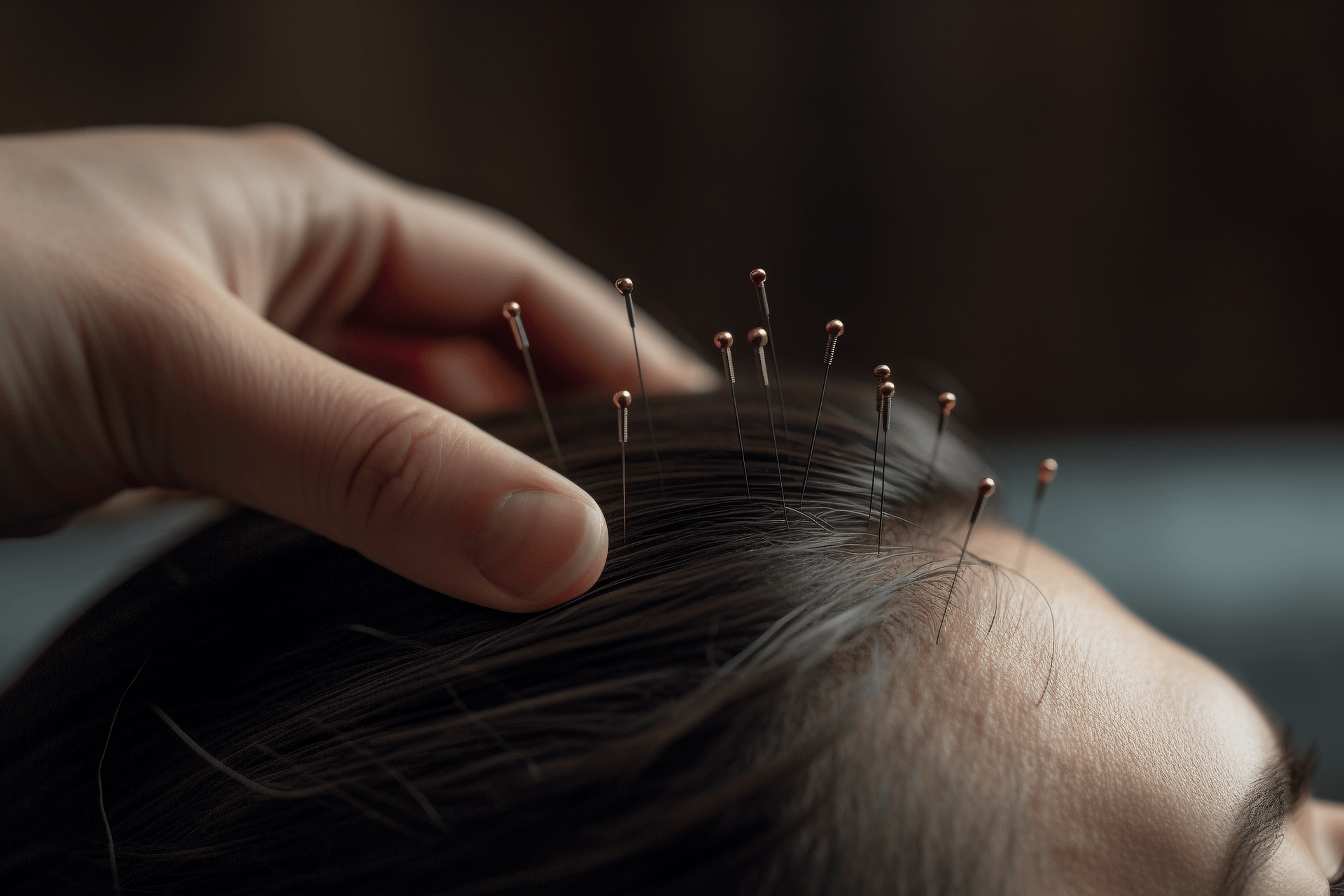
During a normal acupuncture treatment, patients may experience slight pain when the needle is inserted, as well as sensations of soreness, numbness, heaviness, swelling, or comfort in the local area or throughout the body. These sensations are generally tolerable for most people. However, if a patient feels mentally tired, dizzy, nauseous, or even experiences symptoms such as pale complexion, palpitations, sweating, or sudden fainting during the acupuncture process, it is considered acupuncture syncope. It is generally believed that this is caused by temporary cerebral ischemia and hypoxia due to various reasons. For patients receiving acupuncture treatment for the first time, they may be nervous and hungry during the treatment, or they may have a weak constitution due to excessive sweating, diarrhea, or bleeding. In addition, the use of a standing or sitting position during acupuncture can also contribute to the occurrence of syncope. Other factors that can cause syncope during acupuncture include excessive forceful needling technique by the acupuncturist, poor environment in the treatment room, and stuffiness or coldness.
When syncope occurs, it is important to promptly remove all needles from the patient's body, help the patient lie flat, lower the head, loosen clothing, ensure ventilation and warmth, or provide the patient with warm water to drink. The syncope symptoms generally disappear within a few minutes. For those who experience fainting, pressing the "renzhong" or "neiguan" acupoints, or needling or moxibustion at "baihui," "guanyuan," or "shenque" points can be effective. If necessary, modern first aid measures can be used to quickly restore normalcy.